Draft
Notes for byteir code review
[TOC]
Frontend
Byteir支持三种前端输入,分别是onnx,tf,torch,最终收敛到stablehlo dialect。
frontends/
├── README.md
├── onnx-frontend
├── tf-frontend
└── torch-frontend
onnx/tf-frontend
onnx-tf-frontend
其中onnx前端bridge基于开源的onnx-mlir实现,onnx-mlir支持从onnx到tosa或者stablehlo的转换。byteir在前端bridge的实现上,尽量将基础功能同步在upstream中,本地逻辑更多是组织pipeline进行不同前端的转换。
onnx-frontend的实现结构如下:
frontends/onnx-frontend/onnx-frontend/src/
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── Compiler
├── Conversion
├── Support
├── onnx-frontend-opt.cpp
└── onnx-frontend.cpp
实现了离线的编译工具以及opt工具。Compiler路径下主要是封装了onnx to hlo的pipeline,用于给pass manager添加用于conversion的passes。在onnx-mlir namespace下的是upstream中的pass,onnx-frontendnamespace下的则是byteir本地实现的pass。
byteir/frontends/onnx-frontend/onnx-frontend/src/Compiler/OFCompilerPipelines.cpp:
void addCustomizedONNXToStablehloPasses(
mlir::PassManager &pm, const std::vector<std::string> &customCallOps,
bool enableUnroll) {
// Statically add passes for shape inference
for (int i = 0; i < onnx_frontend::ofRepeatStatic; i++) {
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
pm.addPass(onnx_frontend::createOFCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_mlir::createConstPropONNXToONNXPass());
}
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
// convert coarse-grained onnx ops to byteir.xxx custom calls
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_frontend::createOFRewriteCustomOnnxOpsPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_frontend::createOFRewriteToCustomCallPass(customCallOps));
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_mlir::createDecomposeONNXToONNXPass("stablehlo"));
for (int i = 0; i < onnx_frontend::ofRepeatStatic; i++) {
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
pm.addPass(onnx_frontend::createOFCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_mlir::createConstPropONNXToONNXPass());
}
}
// There are more opportunities for const propagation once all tensors have
// inferred shapes.
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_mlir::createConstPropONNXToONNXPass());
if (onnx_frontend::ofRepeatDynamicMax > 0) {
// Dynamic iterate in ONNXOpTransformPass
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createONNXOpTransformPass(
onnx_frontend::ofRepeatStatic, /*report=*/false, false, false, true,
false));
} else {
// Statically add extra passes
for (int i = 0; i < onnx_frontend::ofRepeatStatic; i++) {
pm.addPass(onnx_frontend::createOFCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
onnx_mlir::createConstPropONNXToONNXPass());
}
}
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createStandardFuncReturnPass());
// Clean dead code.
pm.addPass(mlir::createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(onnx_frontend::createOFModifyEntryPointPass());
pm.addPass(onnx_mlir::createLowerToStablehloPass(enableUnroll));
pm.addPass(onnx_frontend::createOFCanonicalizerPass());
(void)mlir::applyPassManagerCLOptions(pm);
mlir::applyDefaultTimingPassManagerCLOptions(pm);
}
整个pipeline包含几个stage:
- infer shape. 重复添加(默认70次)shape inference pass
- 将大粒度算子转换到
hlo的custom call. byteir对stablehlo的扩展是通过 custom call 机制实现的,如扩展 softmax等。前端表达应该最大力度控制ops set的发散,还是允许扩展重要的大粒度op?大部分人选择了后者,这对编译优化提供了方便。当然也有人寄希望于在中后端compiler中搞定所有的事。 - 常量折叠、推导. 主要尝试用
createONNXOpTransformPass在onnx graph level做点优化。这个pass的逻辑主要是在做Decompose,Recompose,shape infer,const prop等。 - 函数返回值类型推导.
- onnx to hlo.
Conversion路径下则是本地onnx_frontend实现的转换pass,主要就是custom call ops的转换。
tf bridge是基于tensorflow实现的,所以用了bazel去编译。之前项目中用tf提供的API搭过类似的bridge,tf内部支持转到tosa或者mhlo。调用tensorflow::ConvertSavedModelToMlir将saved model(GraphDef)转换到mlir moduleOp,然后执行lowering的pipeline将tf graphdef转换到tosa/hlo,如下是转换到tosa的pipeline:
void buildTFImportPassPipeline(OpPassManager &pm) {
// TF standard pipeline
pm.addPass(createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(tf_executor::CreateTFExecutorGraphPruningPass());
pm.addPass(TF::CreateGuaranteeAllFuncsOneUsePass());
TF::CreateTFStandardPipeline(pm, TF::StandardPipelineOptions());
pm.addPass(TF::CreateDeviceIndexSelectorPass());
pm.addPass(createInlinerPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(TFDevice::CreateDecomposeResourceOpsPass());
pm.addPass(TF::CreateTFShapeInferencePass());
// Lower control flow to CFG
pm.addPass(TF::CreateTFFunctionalControlFlowToCFG());
pm.addPass(createInlinerPass());
pm.addPass(createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
// Legalize to TOSA
tosa::TOSATFLegalizationPipelineOptions tosaOptions;
tosa::createTFtoTOSALegalizationPipeline(pm, tosaOptions);
pm.addPass(createInlinerPass());
// after shape infer pass applied
// pm.addNestedPass<FuncOp>(compiler::createLoweringToLibraryCallPass());
pm.addPass(createVerifyFullyConvertedPass());
}
而byteir则是调用tensorflow::GraphdefToMlirTranslateFunction将GrapgDef翻译到mlir module,然后调用mlir::tfext::createCustomizedTfToMhloPipelinePass lower到mhlo以及custom call。CustomizedTfToMhloPipelinePass:
tf to mhlo pipeline
void runOnOperation() override {
auto m = getOperation();
PassManager pm(m->getContext());
pm.addPass(mlir::createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createSCCPPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
// prun useless tf node
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tf_executor::CreateTFExecutorGraphPruningPass());
if (removeControlFlow) {
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createTFSwitchMergeToIfPass());
}
// prun useless tf node
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tf_executor::CreateTFExecutorGraphPruningPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createInlinerPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::TF::CreateDropWhileShapeInvariantPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
// The SCCP pass performs constant propagation across the IR, which, for
// example, propagates constant arguments into callee functions.
// TOOD(hinsu): Investigate if we really need SCCP pass before shape
// inference and can do with just one pass after the shape inference.
pm.addPass(mlir::createSCCPPass());
// Guarantee all functions have one use, which enables shape inference.
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateGuaranteeAllFuncsOneUsePass());
// Run shape inference pass before tensorlist decomposition to get buffer
// shape of uninitialized TensorLists.
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTFShapeInferencePass());
// Run SCCP pass again as the availability of shapes may open up new
// opportunities for constant propagation. Note that the shape inference
// pass doesn't materialize new constants even if those are computed
// internally for the purpose of shape inference. These constants might be
// required by the legalization passes.
pm.addPass(mlir::createSCCPPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTensorListOpsDecompositionPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateStackOpsDecompositionPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTensorArrayOpsDecompositionPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::TFDevice::CreateDecomposeResourceOpsPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreatePromoteResourcesToArgsPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTFShapeInferencePass());
//// TODO(b/171426148): We cannot completely remove region to functional
//// control flow conversion from this pipeline yet as it causes some unit
//// tests to fail.
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTFRegionControlFlowToFunctional());
// LegalizeTFControlFlow encapsulates arguments for control flow operations
// with a tuple argument which break the assumption of resource lifting
// inside PromoteResourcesToArgs.
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::CreateExecutorDialectToFunctionalConversionPass());
if (staticalizeDynamicShape) {
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createProcessDynamicStitchAsStaticPass());
}
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createReshapeMovedownStringPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createConstantFoldingPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createCSEPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTFShapeInferencePass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(mlir::TF::CreateLowerQuantizedPass());
// fuse dilated conv
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::TFL::CreateIdentifyDilatedConvPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(mlir::tfext::createFuseTFOpsPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::tfext::createRewriteToCustomCallOpsPass(customCallOps));
if (this->stopAfterRewriteCustomCall) {
if (mlir::failed(runPipeline(pm, m))) {
signalPassFailure();
}
return;
}
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createMhloLegalizeTfExtPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::mhlo::createLegalizeTFPass(
/*legalize_chlo=*/true,
/*tf2xla_fallback_device_type=*/std::nullopt, false));
pm.addPass(mlir::mhlo::CreateLegalizeTFCommunicationPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
// Run shape inference pass to propagate shapes through tensor_cast
// operations from static to dynamic shapes. This could be generated if the
// shape inference was originally missing in a TF op but the corresponding
// HLO op had static shape after lowering.
pm.addPass(mlir::TF::CreateTFShapeInferencePass());
// Run LegalizeTFPass again because the previous legalization passes can
// expose more graph pruning and canonicalization opportunities that are
// necessary for the second LegalizeTFPass(allow_partial_conversion=false)
// invocation.
pm.addPass(mlir::tfext::createRewriteToCustomCallOpsPass(customCallOps));
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createMhloLegalizeTfExtPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::mhlo::createLegalizeTFPass(
/*legalize_chlo=*/true,
/*tf2xla_fallback_device_type=*/std::nullopt, false));
// if (CanInlineFunctionsPostLegalization(device_type))
// pm.addPass(mlir::createInlinerPass());
// In order to export to XLA, we must sink constants to control flow
// regions, since XLA uses functional control flow.
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::mhlo::createSinkConstantsToControlFlowPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createCSEPass());
// Sparse Conditional Constant Propagation
pm.addPass(mlir::createSCCPPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::tfext::createRewriteToCustomCallOpsPass(customCallOps));
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createMhloLegalizeTfExtPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::mhlo::createLegalizeTFPass(
/*legalize_chlo=*/true,
/*tf2xla_fallback_device_type=*/std::nullopt, false));
pm.addPass(mlir::createInlinerPass());
// Fallback pass to lower all ops that are not legalized to mhlo
// to mhlo::custom_call or ace::custom_call, this pass must be after all
// LegalizeTFPass
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createTfFallbackToCustomCallPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createRewriteFuncAttrToByteIRPass(
additional_main_func_attrs));
if (setAssumingToBeTrue) {
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::createRemoveShapeConstraintsPass());
pm.addNestedPass<mlir::func::FuncOp>(
mlir::tfext::createRemoveCstrReshapablePass());
}
pm.addPass(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(mlir::mhlo::createHloLegalizeToStablehloPass());
if (mlir::failed(runPipeline(pm, m))) {
signalPassFailure();
}
}
torch-frontend
torch-frontend
代码结构如下:
frontends/torch-frontend/torch-frontend/
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── include
│ ├── torch-frontend
│ └── torch-frontend-c
├── lib
│ ├── CAPI
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── Conversion
│ ├── CustomOp
│ ├── Pipelines
│ ├── Transforms
│ └── Utils
├── python
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── csrc
│ ├── gen_version.py
│ ├── setup.py
│ ├── test
│ ├── torch_frontend
│ └── version.txt
└── tools
├── CMakeLists.txt
└── torch-frontend-opt.cpp
核心的pass是放在torch-mlir中实现的,少量pass在byteir本地实现,如Conversion和Transforms路径下的pass。记得早先在项目中支持torch-mlir时并没有torch to mhlo的路线,只有tosa和linalg,后面byteir团队对这条路线做了工作。不同于tf,torch-frontend 最外层的 interface 是用 python 写的,和torch-mlir对外提供的接口相似。torch-mlir translate的路线是 torchscript ir到 torch dialect,然后分发到 tosa/mhlo/linalg 等 dialect。其中 torchscript 需要先经过 functionalization,然后translate到 torch dialect。但是对于 dynamo 抓到的 subgraph(fx graph),是已经 functionalize 过的,所以可以直接translate到 torch dialect。在早先的项目中,尝试的方案是先将 fx graph 序列化到类似GraphDef的表达(pytorch社区有人问过fx graph是否有C++的实现,这应该是对该问题一种实践),然后在C++中使用 MLIR 的 OpBuilder 进行GraphDef到 torch dialect的翻译。当然,byteir是将这个过程放在python上下文中完成的。
fx graph 序列化
syntax = "proto2";
package fx_graph_cpp;
/*
** TODO Support more torch data type as needed.
** Ref(https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html)
*/
enum TorchDataType {
/*
** 32-bit float
*/
FLOAT = 0;
FLOAT32 = 1;
/*
** 64-bit float
*/
FLOAT64 = 2;
DOUBLE = 3;
/*
** 32-bit int
*/
INT = 4;
INT32 = 5;
/*
** 64-bit int
*/
INT64 = 6;
LONG = 7;
/*
** Bool
*/
BOOL = 8;
/*
** 16-bit float
*/
FLOAT16 = 9;
UINT8 = 10;
}
/*
** Ref(https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensor_attributes.html)
*/
enum TorchDataFormat {
/*
** Default to NCHW/NCDHW
*/
CONTIGUOUS_FORMAT = 0;
/*
** NHWC
*/
CHANNELS_LAST = 1;
/*
** NDHWC
*/
CHANNELS_LAST_3D = 2;
/*
** TODO
*/
PRESERVE_FORMAT = 4;
}
enum FxConstantType {
CONST_SCALAR = 0;
CONST_LIST = 1;
CONST_TENSOR = 2;
}
message Device {
enum DeviceType {
UNKNOWN = 0;
CPU = 1;
CUDA = 2;
MUSA = 3;
}
optional DeviceType device_type = 1;
optional int32 device_id = 2;
optional string device_name = 3;
}
message FakeTensor {
optional Device device = 1;
repeated int32 shape = 2;
optional TorchDataType dtype = 3;
}
message TensorMetadata {
repeated int32 shape = 1;
repeated int32 stride = 2;
optional TorchDataType dtype = 3;
optional bool requires_grad = 4;
optional bool is_quantized = 5;
optional TorchDataFormat memory_format = 6;
}
message NodeMeta {
optional string stack_trace = 1;
optional string source_fn = 2;
optional string nn_module_stack = 3;
repeated FakeTensor val = 4;
optional TensorMetadata tensor_meta = 5;
}
enum OpCodeTy {
PLACEHOLDER = 0;
GETATTR = 1;
CALLFUNCTION = 2;
CALLMODULE = 3;
CALLMETHON = 4;
OUTPUT = 5;
CONSTANT = 6;
LIST = 7;
CONSTANT_TENSOR = 8;
}
/*
** ``placeholder`` represents a function input. The ``name`` attribute specifies
** the name this value will take on. ``target`` is similarly the name of the
** argument. ``args`` holds either: 1) nothing, or 2) a single argument denoting
** the default parameter of the function input. ``kwargs`` is don't-care.
** Placeholders correspond to the function parameters (e.g. ``x``) in the graph
** printout.
** ``PlaceHolderNode``. ``args`` are names of ConstantNode
*/
message PlaceHolderNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required string target = 3;
repeated string users = 4;
optional NodeMeta meta = 5;
optional string args = 6;
}
/*
** ``get_attr`` retrieves a parameter from the module hierarchy. ``name`` is
** similarly the name the result of the fetch is assigned to. ``target`` is the
** fully-qualified name of the parameter's position in the module hierarchy.
** ``args`` and ``kwargs`` are don't-care
** TODO
*/
message GetAttrNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required string target = 3;
}
/*
** ``call_function`` applies a free function to some values. ``name`` is similarly the
** name of the value to assign to. ``target`` is the function to be applied. ``args``
** and ``kwargs`` represent the arguments to the function, following the Python calling
** convention
** ``CallFunctionNode``. ``inputs``, ``args``, ``users`` are names of nodes. ``args``
** contanis ``inputs`` and ``constants``
*/
message CallFunctionNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required string target = 3;
repeated string inputs = 4;
repeated string args = 5;
map<string, string> kwargs = 6;
repeated string users = 7;
optional NodeMeta meta = 8;
}
/*
** ``call_module`` applies a module in the module hierarchy's ``forward()``
** method to given arguments. ``name`` is as previous. ``target`` is the
** fully-qualified name of the module in the module hierarchy to call. ``args``
** and ``kwargs`` represent the arguments to invoke the module on, excluding
** the self argument.
** TODO
*/
message CallModuleNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required string target = 3;
/*
** optional Node = args = 4;
*/
}
/*
** ``call_method`` calls a method on a value. ``name`` is as similar. ``target``
** is the string name of the method to apply to the ``self`` argument. ``args``
** and ``kwargs`` represent the arguments to invoke the module on, including
** the self argument
** TODO
*/
message CallMethodNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required string target = 3;
/*
** optional Node = args = 4;
*/
}
/*
** ``output`` contains the output of the traced function in its ``args[0]``
** attribute. This corresponds to the "return" statement in the Graph printout.
** ``OutputNode``. ``outputs`` is names list of output nodes.
*/
message OutputNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required string target = 3;
repeated string outputs = 4;
}
/*
** ``constant`` contains constant as args.
*/
message ConstantNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
/*
** Store all const val as double.
*/
repeated double values = 3;
required TorchDataType dtype = 4;
required FxConstantType ctype = 5;
}
/*
** ``list`` contains list of nodes as a arg. ``name`` is name of current
** node. ``nodes`` is the
** names of nodes inside the list.
*/
message ListNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
repeated string nodes = 3;
}
message ConstTensorNode {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
required string name = 2;
required TorchDataType dtype = 3;
required FxConstantType ctype = 4;
repeated int32 shape = 5;
repeated double values = 6;
}
message Node {
required OpCodeTy opcode = 1;
oneof node {
PlaceHolderNode placeholder_node = 2;
GetAttrNode get_attr_node = 3;
CallFunctionNode call_function_node = 4;
CallModuleNode call_module_node = 5;
CallMethodNode call_method_node = 6;
OutputNode output_node = 7;
ConstantNode constant_node = 8;
ListNode list_node = 9;
ConstTensorNode const_tensor_node = 10;
}
}
Python level pipeline
frontends/torch-frontend/torch-frontend/python/
├── CMakeLists.txt |
├── csrc |
│ └── TorchFrontendModule.cpp | 定义 pybind11 extension 模块,注册 bridge 需要的 pass 和 pipeline
├── gen_version.py |
├── setup.py |
├── torch_frontend |
│ ├── __init__.py | import torch-mlir/frontend 等模块
│ ├── _torch_frontend_registry.py |
│ ├── compile.py | 封装 compile/compile_dynamo_model 接口,将 fx graph 或 nn.Module 转换为 mhlo 的表达
│ ├── flash_attn_op.py | helper function,替换 sdpa 为 flash_attn
│ ├── fx_rewrite.py | fx graph 图优化
│ ├── fx_tracer.py | Tracer,用于符号执行,将 torch.nn.Module 转换为 fx graph
│ ├── fx_utils.py | fx graph 相关的 pattern match 或 rewrite
│ └── ts_utils.py | torchscript 相关的 rewrite
└── version.txt |
-
custom ops set 指定这些 ops 不用decompose或recompose,透传到 mhlo 的 custom call。
_CUSTOM_OPS_IN_TORCH = [ "aten._softmax", "aten.softmax.int", "aten._log_softmax", "aten.log_softmax.int", "aten.native_layer_norm", "aten.layer_norm", "aten.group_norm", "aten.native_group_norm", "aten.gelu", "aten.argmax", "aten.max.dim", "aten.one_hot", "aten.topk", "byteir.flash_attn_fwd", "byteir.flash_attn_bwd", ] -
torch_frontend.compile 复用 torch-mlir 的 compile 接口(
torchscript-module-to-torch-backend-pipeline),将nn.Moduletranslate 到 符合backend contract的 torchscript ir,这一步其实非常繁琐:
void mlir::torch::Torch::createTorchScriptModuleToTorchBackendPipeline(
OpPassManager &pm, const TorchLoweringPipelineOptions &options) {
// When we import TorchScript IR, we import their entire "compilation unit",
// which can contain numerous functions unrelated to the current program,
// which breaks torch-globalization-pipeline; for example, there can be
// random functions referencing types that haven't been imported
// as part of the root `torch.nn.Module` we imported. Those will
// be unreferenced private functions which symbol-dce will clean up nicely.
pm.addPass(createSymbolDCEPass());
// Globalize the program. The rest of the compiler assumes a globalized
// program, which makes all analyses and transforms significantly easier
// to write.
pm.addPass(createPrepareForGlobalizeObjectGraphPass());
pm.addPass(createGlobalizeObjectGraphPass());
// "lower" `torch.global_slot` ops by deleting them if unused, which we
// currently require because we don't have a lowering path for backends to
// handle them.
// Torch usually inserts a few unused global slots so this ends up hitting
// every single module even if it doesn't have any explicit slots.
// TODO: Support global slots in backends.
pm.addPass(createSymbolDCEPass());
// Currently, our shape inference is not powerful enough to deal with
// calls, so inline everything.
// TODO: Improve shape inference.
pm.addPass(createInlinerPass());
createTorchFunctionToTorchBackendPipeline(pm, options);
}
void mlir::torch::Torch::createTorchFunctionToTorchBackendPipeline(
OpPassManager &pm, const TorchLoweringPipelineOptions &options) {
// Incorporate user annotations and remove signature Python-isms.
pm.addPass(createAdjustCallingConventionsPass());
// Perform the bulk of lowering to the backend contract.
// See the pass documentation for more information.
pm.addPass(createLowerToBackendContractPass(
options.maxIterations, options.decompose, options.backendLegalOps,
options.extraLibrary));
}
然后使用 PassManager 先将 torchscript ir lower(torchscript-to-torch-pipeline)到 torch dialect;以及通过torch-to-mhlo-pipeline lower 到 mhlo。
-
torch_frontend.compile_dynamo_model 输入的 model 类型是 fx graph,
FxImporter.import_graph_module作为 bridge 直接将 fx graph 解析翻译到 mlir module。然后通过 pipelinetorch-function-to-torch-pipeline和torch-to-mhlo-pipeline完成 lowering。 -
FxImporter 这个模块用于支持 torch dynamo(Main entry-point for importing an fx.GraphModule.)。因为 dynamo 抓图后会做 functionalize,所以 fx graph 的nodes按拓扑序排序的,importer只需要遍历nodes逐个翻译即可。对于每个 node,根据其 opcode 做相应的处理。
importer 核心逻辑
def import_nodes(self, nodes: Sequence[torch_fx.Node]): with InsertionPoint(self._b): loc = Location.unknown() num_placeholders = 0 for node in nodes: op = node.op # Attempt to extract locations. Not everything has them, # so we do our best. new_loc = self._cc.get_node_location(node) if new_loc is not None: loc = new_loc if op == "placeholder": # Associate the placeholder node with corresponding block # argument. self._v[(node, 0)] = self._b.arguments[num_placeholders] num_placeholders += 1 elif op == "call_function": target = node.target if target == operator.getitem: # Special case handling of getitem for when it is resolving # against a function call that we know has returned multiple # results. We short-circuit this case because we have modeled # function calls to natively return multiple results vs tupling. getitem_ref, getitem_index = node.args if getitem_ref in self._multi_result_nodes: try: self._v[(node, 0)] = self._v[ (getitem_ref, getitem_index) ] except IndexError: raise RuntimeError( f"getitem de-aliasing failed. This likely " f"indicates a programmer error that usually " f"would have happened at runtime. Please " f"notify developers if this case happens " f"(at {loc})." ) else: raise NotImplementedError( f"General getitem access to non-multi-result ops" ) elif isinstance(target, TorchOpOverload): # Dispatch to an ATen op. self._import_torch_op_overload(loc, node, target) elif target in SYMBOLIC_TORCH_OPS or ( is_symbolic(node.meta.get("val")) and is_builtin_function_or_method(target) ): self._import_symbolic_torch_op(loc, node, target) else: raise NotImplementedError( f"FIX ME: Unimplemented call_function: target={node.target}, {node.meta}" ) elif op == "output": # args[0] is a singleton tuple that we flatten into multiple # results. operands = [self._import_argument(loc, arg) for arg in node.args[0]] func_dialect.ReturnOp(operands, loc=loc)早先实现过类似的功能(:
/*static*/ mlir::OwningOpRef<mlir::ModuleOp> FxGraphParserImpl::ConvertFxGraphToTorch(const std::string &sg, Arguments &args, CodeGenOpts &opts) { // FIXME(chhuang) Why do we need to reset MLIRContext everytime? setMLIRContext(); fx_graph_cpp::Graph g; if (!g.ParseFromString(sg)) { std::cerr << "decode sg fail\n"; } if (opts.disable_threading) context_.disableMultithreading(true); // TODO gen func info. not hard-coded here. mlir::Attribute debugModuleNameAttr = mlir::StringAttr::get(&context_, "grace_torch_module"); std::string entry_name("serving_default"); mlir::Location loc = mlir::Location(mlir::UnknownLoc::get(&context_)); mlir::ModuleOp module = mlir::ModuleOp::create(loc); module->setAttr("torch.debug_module_name", debugModuleNameAttr); mlir::OpBuilder builder(&context_); mlir::Region ®ion = module.getBodyRegion(); builder.setInsertionPointToStart(®ion.front()); FxName2OpMap name2op_map; FxName2NodeMap name2node_map; // Create mlir funcOp // FIXME make sure the in/output order in the graph is same with // example_inputs. llvm::SmallVector<mlir::Type> arg_types; llvm::SmallVector<mlir::Type> res_types; llvm::SmallVector<const fx_graph_cpp::PlaceHolderNode *> placeholder_nodes; llvm::SmallVector<const fx_graph_cpp::CallFunctionNode *> call_function_nodes; llvm::SmallVector<const fx_graph_cpp::OutputNode *> output_nodes; llvm::SmallVector<const fx_graph_cpp::ConstantNode *> constant_nodes; llvm::SmallVector<const fx_graph_cpp::ListNode *> list_nodes; llvm::SmallVector<const fx_graph_cpp::ConstTensorNode *> const_tensor_nodes; // One could not get returnOp's info in the first time. In the first stage, // creates a function body without return value; in the second stage, creates // all nodes inside function body; in the third stage, gets output info and // reset function type with input/output info. // Stage 1. // args.entry_func.append(sg); for (auto &node : g.nodes()) { switch (node.opcode()) { case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::PLACEHOLDER: { name2node_map[node.placeholder_node().name()] = &node; auto &tensor_meta = node.placeholder_node().meta().tensor_meta(); arg_types.push_back(getFxTensorType(&context_, tensor_meta)); } placeholder_nodes.push_back(&node.placeholder_node()); break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::OUTPUT: name2node_map[node.output_node().name()] = &node; output_nodes.push_back(&node.output_node()); break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLFUNCTION: name2node_map[node.call_function_node().name()] = &node; call_function_nodes.push_back(&node.call_function_node()); // args.entry_func.append(node.call_function_node().name()); break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CONSTANT: constant_nodes.push_back(&node.constant_node()); // args.entry_func.append(node.constant_node().name()); break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::LIST: list_nodes.push_back(&node.list_node()); // args.entry_func.append(node.list_node().name()); break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::GETATTR: name2node_map[node.get_attr_node().name()] = &node; break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CONSTANT_TENSOR: const_tensor_nodes.push_back(&node.const_tensor_node()); break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLMODULE: // break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLMETHON: // break; default: llvm::errs() << "Unsupported opcode in stage 1:\n" << node.DebugString() << "\n"; break; } } res_types.clear(); // FIXME One should make a resumption that subgraph exported from dynamo has // and only has one function(block). FunctionType functype = builder.getFunctionType(arg_types, res_types); auto funcOp = builder.create<func::FuncOp>(loc, entry_name, functype); Block *func_block = funcOp.addEntryBlock(); builder.setInsertionPointToEnd(&funcOp.getBody().front()); for (int64_t idx = 0; idx < placeholder_nodes.size(); ++idx) { name2op_map[placeholder_nodes[idx]->name()] = funcOp.getArgument(idx); } // Stage 2. Add nodes. for (auto &node : g.nodes()) { Value new_node; switch (node.opcode()) { case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::PLACEHOLDER: case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::OUTPUT: break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLFUNCTION: new_node = createTorchOpNode(builder, &context_, &node.call_function_node(), name2op_map); name2op_map[node.call_function_node().name()] = new_node; break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CONSTANT: new_node = createTorchConstantNode(builder, &context_, &node.constant_node()); name2op_map[node.constant_node().name()] = new_node; break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::LIST: new_node = createTorchListArgNode(builder, &context_, &node.list_node(), name2op_map); name2op_map[node.list_node().name()] = new_node; break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::GETATTR: break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CONSTANT_TENSOR: new_node = creareTorchConstTensorNode(builder, &context_, &node.const_tensor_node()); name2op_map[node.const_tensor_node().name()] = new_node; break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLMODULE: // break; case fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLMETHON: // break; default: llvm::errs() << "Unsupported opcode in stage 2:\n" << node.DebugString() << "\n"; break; } } // convert proto deviceTy to mtrt deviceTy. auto setDeviceTy = [](const fx_graph_cpp::Device &device) { switch (device.device_type()) { case fx_graph_cpp::Device::CPU: return DeviceType::CPU; case fx_graph_cpp::Device::MUSA: return DeviceType::MUSA; case fx_graph_cpp::Device::CUDA: return DeviceType::CUDA; default: return DeviceType::UNKNOWN; } }; // Stage 3. Append ReturnOp(which is required). assert(output_nodes.size() == 1 && "Invalid number output_nodes"); llvm::SmallVector<Value> res_values; for (auto &out_val_name : output_nodes[0]->outputs()) { DeviceType _deviceType; const fx_graph_cpp::NodeMeta *node_meta = NULL; if (name2node_map[out_val_name]->opcode() == fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::CALLFUNCTION) node_meta = &name2node_map[out_val_name]->call_function_node().meta(); else if (name2node_map[out_val_name]->opcode() == fx_graph_cpp::OpCodeTy::PLACEHOLDER) node_meta = &name2node_map[out_val_name]->placeholder_node().meta(); else assert(0 && "Invalid output nodes opcode"); if (node_meta->val_size() == 0) { llvm::errs() << "op set device err\n"; } else { _deviceType = setDeviceTy(node_meta->val(0).device()); } Value out_val = name2op_map[out_val_name]; res_values.push_back(out_val); res_types.push_back(out_val.getType()); // FIXME may return scalar type. // if (auto resTensorType = // out_val.getType().dyn_cast<Torch::BaseTensorType>()) { // auto res_shape = resTensorType.getSizes(); // std::vector<int64_t> _shape(res_shape.begin(), res_shape.end()); // Type resElementTy = resTensorType.getDtype(); // DataType _dtype = FxGraphParserImpl::mapMlirDType2Grace(resElementTy); // std::vector<int64_t> _stride; // _stride.reserve(node_meta->tensor_meta().stride_size()); // for (auto s : node_meta->tensor_meta().stride()) { // _stride.push_back(s); // } // args.outputs.push_back( // std::move(MetaTensor(_dtype, _shape, _stride, 0, _deviceType))); // } else { // llvm::report_fatal_error( // "Unsupport result type, only expect Torch::BaseTensorType yet"); // } } // Update FunctionType, as missing return info before. FunctionType new_functype = builder.getFunctionType(arg_types, res_types); funcOp.setFunctionType(new_functype); builder.setInsertionPointToEnd(&funcOp.getBody().front()); builder.create<func::ReturnOp>(loc, res_values); llvm::raw_string_ostream os(args.entry_func); module.print(os); return mlir::OwningOpRef<mlir::ModuleOp>(module); } -
replace_flash_attngraph level 的op优化,尝试将 fx graph 中sdpa替换为CustomFlashAttnFunc(当没有mask且是causal的),替换后的实现如下:
@op("byteir::flash_attn_fwd(Tensor q, Tensor k, Tensor v, float dropout_p, float softmax_scale, bool casual, bool return_softmax) -> (Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor)")
def byteir_flash_attn_fwd(q, k, v, dropout_p, softmax_scale, causal, return_softmax):
sizes = q.shape
batch_size = sizes[0]
seqlen_q = sizes[1]
num_heads = sizes[2]
seqlen_k = k.shape[1]
rng = torch.empty((2), dtype=torch.int64, device='meta')
softmax_lse = torch.empty(
(batch_size, num_heads, seqlen_q), dtype=torch.float, device='meta')
p = None
if (return_softmax):
p = torch.empty((batch_size, num_heads, seqlen_q,
seqlen_k), dtype=torch.float, device='meta')
q_padded = q
k_padded = k
v_padded = v
out = torch.empty_like(q_padded)
out_padded = torch.empty_like(out)
return out, q_padded, k_padded, v_padded, out_padded, softmax_lse, p, rng
@op("byteir::flash_attn_bwd(Tensor dout, Tensor q, Tensor k, Tensor v, Tensor out, Tensor softmax_lse, float dropout_p, float softmax_scale, bool casual, Tensor rng) -> (Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, Tensor)")
def byteir_flash_attn_bwd(dout, q, k, v, out, softmax_lse, dropout_p, softmax_scale, causal, rng_state):
sizes = q.shape
batch_size = sizes[0]
seqlen_q = sizes[1]
num_heads = sizes[2]
seqlen_q_rounded = ((seqlen_q+127)//128)*128
head_size = sizes[3]
head_size_rounded = ((head_size+31)//32)*32
dq_accum = torch.empty((batch_size, num_heads, seqlen_q_rounded, head_size_rounded), dtype=torch.float, device='meta')
softmax_d = torch.empty((batch_size, num_heads, seqlen_q_rounded), dtype=torch.float, device='meta')
dq = torch.empty_like(q)
dk = torch.empty_like(k)
dv = torch.empty_like(v)
return dq, dk, dv, softmax_d, dq_accum
其实是返回empty tensor,因为这里只是想透传 flashattn 到 mhlo,并不需要具体的实现。
-
fx_replace_attn_patterngraph level pattern match and rewrite.def fx_replace_attn_pattern(gm: torch.fx.GraphModule): gm = canonicalize_graph_before_replacement(gm) # Need hf_symbolic_trace to trace torch.full torch.fx.replace_pattern(gm, hf_symbolic_trace(AttnPattern), AttnReplacement) torch.fx.replace_pattern(gm, AttnPattern1, AttnReplacement1) torch.fx.replace_pattern(gm, AttnPattern2, AttnReplacement2) torch.fx.replace_pattern(gm, AttnPattern3, AttnReplacement3) torch.fx.replace_pattern(gm, AttnPattern4, AttnReplacement4) torch.fx.replace_pattern(gm, AttnPattern5, AttnReplacement5) return gm针对各个LLM中的attn的pattern去匹配并重写attn算子,替换为
torch.ops.aten.scaled_dot_product_attention。 GPT2 中 attn 的 pattern如下:# GPT2 Attention patterns def AttnPattern(query, key, value, causal_mask, mask_value, inv_scale, device, dropout_p): attn_weights = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-1, -2)) attn_weights = attn_weights / torch.full( [], inv_scale, dtype=torch.float16, device=device ) attn_weights = torch.where(causal_mask, attn_weights.to(torch.float16), mask_value) attn_weights = torch.nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1) attn_weights = attn_weights.type(torch.float16) attn_weights = torch.nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=dropout_p) attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value) return attn_output不妨再关注一下 fx 提供的 match and rewrite infra:
SubgraphMatcher将input nodes 或 output nodes 作为 candidate anchor,用回溯算法逐个去尝试match 给定的 pattern。SubgraphMatcher.match
def match(self, graph: Graph) -> List[InternalMatch]: """ Returns: The matched subgraphs. Thre returned subgraph would be fully self-contained, meaning the nodes (except placeholder and nodes returned by output) can only be consumed by nodes within the matched subgraph. Subgraph pattern matcher is implemented with the backtracking style in the following steps: 1. We first identify all the anchor nodes in the pattern graph. The anchor nodes are the "sinks" (nodes with no user other than the output node) of the pattern graph. One pattern graph could have multiple anchors if it has multiple return values. 2. In the target graph, we identify the potential candidate nodes that can be matched with each anchor. These anchor-candidate pairs are the starting points for pairwise per-node matching. 3. For each anchor-candidate pair, we simultaneously traverse backwards (DFS) in both pattern and target graphs. For every pattern nodes along traversal path, we compare it against the target nodes. In case any comparison failed, the match for this anchor-candidate pair fails. A match is found when DFS completes traversing the graph. See `self._match_nodes` for more details. 4. In the case of multiple anchors, every anchor will need to find a match using step 3. In addition, the matches found between anchors need to have a common intersection node in order for the match to be valid. This is implemented with backtracking. See `backtracking` for more details. Notice: graph traversal must be done in the reverser order because a tensor can have multiple consumers, but can only have a single producer. Only with reverser order, we can we jointly traverse the pattern and target graph in a deterministic path. Warning: In theory, this backtracking algorithm have an **exponential** time complexity. However, in practice, it's unlikely to blow up. """ from torch.fx.passes.utils.fuser_utils import validate_partition # find candidate nodes to match with pattern anchors match_candidates: Dict[Node, List[Node]] = defaultdict(list) for pattern_anchor in self.pattern_anchors: for node in graph.nodes: if self._nodes_are_equal(pattern_anchor, node): match_candidates[pattern_anchor].append(node) match_candidates_list = list(match_candidates.items()) logger.info("Initial match_candidates_list: %s\n", match_candidates_list) matches: List[InternalMatch] = [] def backtracking(anchor_index, match): if anchor_index == len(match_candidates_list): match.placeholder_nodes = [match.nodes_map[pn] for pn in self.pattern_placeholder_nodes] match.returning_nodes = [match.nodes_map[pn] for pn in self.pattern_returning_nodes] matches.append(match) logger.info("Found a match: %s\n", match) return pattern_anchor, candidate_nodes = match_candidates_list[anchor_index] saved_match = copy.copy(match) for node in candidate_nodes: logger.info("Trying to match anchor %s to %s", pattern_anchor, node) match_found = self._match_nodes(pattern_anchor, node, match) if match_found: # match next anchor backtracking(anchor_index + 1, match) else: logger.info("Failed to match anchor %s to %s\n", pattern_anchor, node) # revert to saved_match before matching with current anchor match = copy.copy(saved_match) match = InternalMatch(anchors=self.pattern_anchors) if match_candidates_list: backtracking(0, match) # filter out the matches where the subgraph is not fully_contained before = len(matches) matches = [match for match in matches if self._is_contained(match.nodes_map)] after = len(matches) if before != after: logger.info("Filtered out %s matches because they are not fully contained", before - after) # filter out the matches that form a cycle if the subgraph is fused valid_matches = [] for match in matches: matched_compute_nodes = \ [gn for pn, gn in match.nodes_map.items() if pn.op not in {"placeholder", "output"}] if validate_partition(matched_compute_nodes): valid_matches.append(match) if len(valid_matches) != len(matches): logger.info("Filtered out %s matches because \ matched subgraph would form a cycle if fused", len(matches) - len(valid_matches)) if self.remove_overlapping_matches: before = len(valid_matches) matches = self._remove_overlapping_matches(valid_matches) after = len(matches) if before != after: logger.info("Filtered out %s matches because matched subgraphs are overlapping", before - after) logger.info("Matches returned: %s", matches) return matches
C++ level core passes implementation
-
torch-to-mhlo-pipelinecreateTorchToMhloPipeline
void mlir::torch_frontend::createTorchToMhloPipeline(OpPassManager &pm) { pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createConvertTorchToCcl()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createConvertTorchToCustomCall()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createConvertTorchToStablehloExt()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createConvertTorchToStablehloPass(false, false)); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createConvertTorchToArithPass()); // Clean up any non-canonical code introduced above.. pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); // The resolution of `dim` ops tends to create identical ops. CSE them. pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCSEPass()); // Clean up any non-canonical code introduced above.. pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); // The resolution of `dim` ops tends to create identical ops. CSE them. pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCSEPass()); // Finish the type conversion from `torch` types to the types of the // MHLO backend contract. pm.addPass(TorchConversion::createFuncBackendTypeConversionPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( TorchConversion::createFinalizingBackendTypeConversionPass()); // Verify that we have lowered to the form that Stablehlo backends // expect. This fails compilation (signalPassFailure) if the IR is not in the // correct form. pm.addPass(TorchConversion::createVerifyStablehloBackendContractPass()); // Perform additional canonicalization, which is not suitable in byteir // pipeline. pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizeExtPass()); } void mlir::torch_frontend::createTorchFunctionToTorchPipeline( OpPassManager &pm, const Torch::TorchLoweringPipelineOptions &options) { // remove useless ops pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createEliminateUselessOpPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); // Unpack return values pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createUnpackPublicFunctionReturnPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); pm.addPass(Torch::createAdjustCallingConventionsPass()); // Rewrite custum ops to Torch.CustomOp pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createRewriteCustomOp()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass()); // Fuse Torch Ops pm.addPass(createCSEPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createFuseOpOnTorch()); pm.addPass(Torch::createLowerToBackendContractPass( options.maxIterations, options.decompose, options.backendLegalOps, options.extraLibrary)); }几个特殊的pass:
-
Conversion
createConvertTorchToCclConvert torch communication ops to byteir ccl dialect. byteir 扩展了 torch dialect,添加了 C10xxx 通信算子,并在byteir中设计了 ccl dialect 用于表达 collective ops。几乎是在一一映射到ccl上。
ConvertC10dFunctionalAllReduceOp
class ConvertC10dFunctionalAllReduceOp : public OpConversionPattern<C10dFunctionalAllReduceOp> { public: using OpConversionPattern<C10dFunctionalAllReduceOp>::OpConversionPattern; LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(C10dFunctionalAllReduceOp op, OpAdaptor adaptor, ConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter) const override { Value input = adaptor.getSelf(); auto outType = getTypeConverter()->convertType(op.getResult().getType()); std::string reduceOp, tag; if (!matchPattern(op.getReduceOp(), m_TorchConstantStr(reduceOp))) { return rewriter.notifyMatchFailure(op, "unsupported value of reduceOp"); } // make sure reduce op is lowercase string. std::transform(reduceOp.begin(), reduceOp.end(), reduceOp.begin(), [](unsigned char c) { return std::tolower(c); }); if (!matchPattern(op.getTag(), m_TorchConstantStr(tag))) { return rewriter.notifyMatchFailure(op, "unsupported value of tag"); } llvm::SmallVector<int64_t> ranks; if (!matchPattern(op.getRanks(), m_TorchListOfConstantInts(ranks))) { return rewriter.notifyMatchFailure(op, "unsupported value of ranks"); } int64_t groupSize; if (!matchPattern(op.getGroupSize(), m_TorchConstantInt(&groupSize))) { return rewriter.notifyMatchFailure(op, "unsupported value of group_size"); } auto cclAllReduceOp = rewriter.create<ccl::AllReduceOp>( op->getLoc(), input, Value(), /*synchronous=*/rewriter.getBoolAttr(false), rewriter.getStringAttr(reduceOp), rewriter.getArrayAttr( ArrayRef<Attribute>{rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr(ranks)}), /*unique_id=*/nullptr); rewriter.replaceOp(op, cclAllReduceOp.getResult()); return success(); } };createConvertTorchToCustomCall粗略的对应前面 bridge 中的 custom opset,将 norm,softmax,flashattn 等算子直接 convert 到 stablehlo 的 custom call。custom call 并不会真的涉及到 optimized implementation,仅仅是构造 input/output 并透传op(具体的算法实现放在compiler中)。createConvertTorchToStablehloExtConvert torch ops to stablehlo extension. 如Aten_IndexPutImplOp,AtenPowScalarOpcreateConvertTorchToStablehloPass
torch to stablehlo
torch_to_stablehlo::TorchToStablehloOptions options{ enableStaticShape, enableI32Index ? 32u : 64u}; torch_to_stablehlo::populateBasicOpPatternsAndLegality( typeConverter, patterns, target, options); torch_to_stablehlo::populateViewLikeOpPatternsAndLegality( typeConverter, patterns, target, options); torch_to_stablehlo::populateGatherScatterOpPatternsAndLegality( typeConverter, patterns, target, options); torch_to_stablehlo::populateReductionOpPatternsAndLegality( typeConverter, patterns, target, options); torch_to_stablehlo::populateLinearOpPatternsAndLegality( typeConverter, patterns, target, options); torch_to_stablehlo::populatePoolingOpPatternsAndLegality( typeConverter, patterns, target, options); -
Transforms
createCanonicalizeExtPass为stablehlo::CustomCallOp实现 dec,这个功能应该最好是放在这个op的 canonicalize 方法中。逻辑很简单,遍历所有op,如果没有 use,且满足wouldOpBeTriviallyDead(upstream的实现,分析是否有side-effect) 或是custom call,则删除。createRewriteCustomOp将byteir自定义的 torch ops 转换为 torch custom ops,而torch custom op 会被转换为 stable custom call.createEliminateUselessOpPasscreateFuseOpOnTorch在torch dialect中针对特殊 pattern 做了 DAG rewrite,用了DRR这种方式去写td。byteir 做了两个 pattern的优化:
fuse on torch
def TorchGeluTanhPattern : Pat< (Torch_AtenMulTensorOp:$output (Torch_AtenMulTensorOp $input, (Torch_NonValueTensorLiteralOp $const_5) ), (Torch_AtenAddTensorOp (Torch_AtenTanhOp (Torch_AtenMulTensorOp (Torch_AtenAddTensorOp $input, (Torch_AtenMulTensorOp (Torch_AtenPowTensorScalarOp $input, (Torch_ConstantIntOp $int3) ), (Torch_NonValueTensorLiteralOp $const_4) ), (Torch_ConstantIntOp $int1_1) ), (Torch_NonValueTensorLiteralOp $const_7) ) ), (Torch_NonValueTensorLiteralOp $const_1), (Torch_ConstantIntOp $int1) ) ), (createGeluTanh $output, $input), [(OneIntegerAttr $int1), (OneIntegerAttr $int1_1), (ThreeIntegerAttr $int3), (Constraint<CPred<"$0.getSplatValue<APInt>() == 1">, ""> $const_1), (Constraint<CPred<"isSplatCloseToValue($0.cast<DenseFPElementsAttr>(), 0.5)">, ""> $const_5), (Constraint<CPred<"isSplatCloseToValue($0.cast<DenseFPElementsAttr>(), 4.471500e-02, 0.0001)">, ""> $const_4), (Constraint<CPred<"isSplatCloseToValue($0.cast<DenseFPElementsAttr>(), 0.797884583, 0.0001)">, ""> $const_7)] >; def createLayerNorm : NativeCodeCall<"createLayerNorm($_builder, $_loc, $0, $1, $2, $3, $4, $5, $6)">; def TorchLayerNormPattern : Pat< (Torch_AtenAddTensorOp:$output (Torch_AtenDivTensorOp (Torch_AtenMulTensorOp $weight, (Torch_AtenSubTensorOp $input, (Torch_AtenMeanDimOp $input, $list, (Torch_ConstantBoolOp $true_value), (Torch_ConstantNoneOp) ), (Torch_ConstantIntOp $int1_2) ) ), (Torch_AtenAddTensorOp (Torch_AtenStdDimOp $input, $list, (Torch_ConstantBoolOp:$false_op $false_value), (Torch_ConstantBoolOp $true_value_1) ), (Torch_NonValueTensorLiteralOp $epsilon), (Torch_ConstantIntOp $int1_1) ) ), $bias, (Torch_ConstantIntOp $int1) ), (createLayerNorm $output, $input, $list, $weight, $bias, (NativeCodeCall<"createLayerNormEpsilon($_builder, $_loc, $0)"> $epsilon), $false_op), [(TrueAttr $true_value), (TrueAttr $true_value_1), (FalseAttr $false_value), (OneIntegerAttr $int1), (OneIntegerAttr $int1_1), (OneIntegerAttr $int1_2)] >;第一个 pattern rewrite 的 source pattern 对应的示例如下:
%mul_0 = "aten.mul"(%input, %const_0.5) %pow = "aten.pow"(%input, %const_3) %mul_2 = "aten.mul"(%pow, %const_4.4715e-02) %add_1 = "aten.add"(%input, %mul_2, %const_1) %mul_1 = "aten.mul"(%add_1, %const_0.797884583) %tanh = "aten.tanh"(%mul_1) %add_0 = "aten.add"(%tanh, %const_1.0, %const_1) %mul = "aten.mul"(%mul_0, %add_0)上面的计算约等于:
%result = "aten.gelu"(%input, %aten_str<"tanh">)比较好奇是怎么推导出来的.
createUnpackPublicFunctionReturnPass
-
stablehlo Spec op set完备性比较好,设计了collective communication ops,也有 custom_call提供扩展机制。 Replace mlir-hlo with stablehlo
Compiler
compiler/
├── cmake
├── dialects | ace 和 ccl dialect 的定义,单独放在外面而非 include 路径下,方便给 frontend 依赖
├── include |
├── lib |
├── python |
├── tools |
Dialect extension
byteir 基于 upstream 的 dialect 进行了扩展,如下:
compiler/include/byteir/Dialect/
├── Ace
├── Affine
├── Byre
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── Cat
├── Ccl
├── GPU
├── Lace
├── Linalg
├── MemRef
├── SCF
├── Shape
├── Tensor
├── Transform
├── Vector
└── mhlo
其中 Ace 和 Ccl 的定义放在外层 compiler 路径下。 Affine 等路径下是对upstream transforms pass的扩展,其他dialect 如:
- Ace 是对 mhlo ops 的扩展
- Byre 是 byteir runtime 的扩展
- Cat 会从 mhlo lower 一部分 ops(如 BMM) 过来,不清楚为什么设计这个 dialect,看着像是会fuse之后 替换成 AIT。
- Ccl Dialect works as a communication collective language in MLIR. 如 Linalg dialect 经过 shared distributed strategy 后引入 ccl 中的 collective communication 算子。
- Lace 是对 lhlo 的补充
Ace
Ccl
Cat
Lace
Byre
Byteir runtime(调度 kernel/func)的op,几个关键 op 如下:
- Byre::ComputeOp. 表示执行一个 kernel
- Byre::ComputeShapeOp. 执行一个 shape 计算的函数,因为只涉及到tensor的 meta info,所以可以提前计算
- Byre::CopyOp. 节点内内存搬移,因为 memref 可以带 memory space 信息,所以可以表达 h2d/d2h 等内存搬移
- Byre::GroupCopyOp. 分布式节点间数据搬移
- Byre::CustomOp. 表示 lib call
为了表达异步计算语义,byre 中定义了 byre::AsyncTokenType。因为不同后端device有各自的 async token,byre应该是做了一层抽象,最终会lower到device对应的dialect上。
Byre 实现了 serialization 机制。
Transforms ext
compilation workflow
byteir 开源版本封装了两种 compile flow,分别是 compile_cuda和 compile_cuda_with_ait,都是给 cuda 后端做codegen。前者是典型的从 linalg -> scf -> gpu -> nvvm -> ptx 的 MLIR based ai compiler compilation flow。后者会将一部分计算图转到 CAT dialect,然后用 ait_builder 替换成 AIT 的实现,其余计算图仍然走 nvvm 的workflow。
byteir.compile 将 compilation 产物落盘在指定的 path 下面,似乎没有看到在这一层做 compilation cache。
从 mlir.cat 到 AIT 的 translation 的实现在 :
compiler/python/byteir/dialects/cat/ir_translator/backend/ait_registry.py
路径下,byteir 为 ait backend 实现了一个建议的 match and rewrite 机制:
compiler/python/byteir/dialects/cat/ir_translator/translator.py
compile_cuda
hlo-opt{outline-single-elemwise-op}linalg-tensor-optbyre-tensor-optbyteir-bufferize-optlinalg-memref-optscf-optgpu-optremove-func-body{anchor-attr=__byteir_elementwise_fusion__}inlinegpu-launch-func-to-byreset-op-spaceset-arg-spacebyre-optnvvm-codegentranslate_to_ptxbyre-host
compile_cuda_with_ait
IRProcessor.preprocess_passIRProcessor.cat_opt_passIRProcessor.hlo_opt_passIRProcessor.ait_opt_passlinalg-tensor-optbyre-tensor-optbyteir-bufferize-optlinalg-memref-optscf-optgpu-optremove-func-bodyinlinegpu-launch-func-to-byreset-op-spaceset-arg-spacebyre-optnvvm-codegentranslate_to_ptxbyre-host
pipeline analysis
decl path: compiler/include/byteir/Pipelines/*.h, compiler/include/byteir/Transforms/Passes.td
def path: compiler/lib/Pipelines/*LinalgTensorOpt*.cpp
hlo-opt
func: createHloOptPipeline
在 hlo dialect 做图优化,包含op折叠和op融合两个部分。 op折叠是根据一些patern将op替换为效率更高的组合:
// generic folding
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createHloFolderPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createHloFolderPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createHloTransposeDotToDotGeneralPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createReduceFusionPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createReshapeGatherPass());
pm.addPass(createConvertOpToCustomCallPass());
op融合则是在hlo中将ops融合到mhlo::FusionOp中:
// add fusion patterns
if (target == "CPU") {
addCPUHloFusionPatterns(pm, entryFunc);
} else {
addGenericHloFusionPatterns(pm, entryFunc, outlineSingleElemwiseOp,
outlineCatOp, aggressiveCatFusion);
}
byteir对hlo op融合抽象出了通用模板,不同类型的融合只需要实现各自的特殊逻辑。
==TODO== deep into this pipeline
linalg-tensor-op
func: createLinalgTensorOptPipeline
-
convert hol to linalg
-
enhance linalg element-wise fusion
-
element-wise kernel codegen
-
reduce kernel codegen
passes
void addGenericLinalgPasses(OpPassManager &pm) { pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createHloFusionToLinalgPass(getByteIRElementwiseFusionAttrName())); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createHloFusionToLinalgPass(getByteIRReductionFusionAttrName())); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createUnrealizedCastToLinalgPass()); pm.addPass(createLinalgElementwiseFusionExtPass( /*enableSharedInput*/ true, /*enableDiffShapes*/ false)); pm.addPass(createCSEPass()); { // elementwise codegen auto elementwiseAnchor = getByteIRElementwiseFusionAttrName().str(); GPUTileElementwiseOptions options; options.funcAnchor = elementwiseAnchor; // set to 1 for fully fusion & unroll, and all tiled loops will be coalesced // and mapping to LinearIdx.x in later pipeline // FIXME: set to real blockSize and mapping tiled loops to the corresponding // parallel dims options.blockSize = 1; options.warpSize = 32; createGPUTileElementwiseTransform(pm, options); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); { OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createLinalgFoldUnitExtentDimsPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createLinalgElementwiseFusionExtPass( /*enableSharedInput*/ true, /*enableDiffShapes*/ false)); anchoredPM.addPass(createCSEPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createAnchoredPipelinePass(elementwiseAnchor, anchoredPM)); } } { // reduction codegen auto reductionAnchor = getByteIRReductionFusionAttrName().str(); { OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName()); anchoredPM.addPass( createLinalgCollapseLoops(utils::IteratorType::reduction)); anchoredPM.addPass( createLinalgCollapseLoops(utils::IteratorType::parallel)); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createAnchoredPipelinePass(reductionAnchor, anchoredPM)); } GPUSplitGridReductionOptions splitGridRedOptions; splitGridRedOptions.funcAnchor = reductionAnchor; createGPUSplitGridReductionTransform(pm, splitGridRedOptions); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); GPUTileGridReductionOptions tileGridRedOptions; tileGridRedOptions.funcAnchor = reductionAnchor; tileGridRedOptions.blockSize = 512; createGPUTileGridReductionTransform(pm, tileGridRedOptions); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); { OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName()); anchoredPM.addPass(createLinalgFoldUnitExtentDimsPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCSEPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createAnchoredPipelinePass(reductionAnchor, anchoredPM)); } GPUSplitBlockReductionOptions splitBlockRedOptions; splitBlockRedOptions.funcAnchor = reductionAnchor; splitBlockRedOptions.splitFactor = 16; createGPUSplitBlockReductionTransform(pm, splitBlockRedOptions); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); GPUTileBlockReductionOptions tileBlockRedOptions; tileBlockRedOptions.funcAnchor = reductionAnchor; tileBlockRedOptions.blockSize = 512; createGPUTileBlockReductionTransform(pm, tileBlockRedOptions); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); { OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName()); anchoredPM.addPass(createLinalgFoldUnitExtentDimsPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCSEPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createAnchoredPipelinePass(reductionAnchor, anchoredPM)); } GPUTileThreadReductionOptions tileThreadRedOptions; tileThreadRedOptions.funcAnchor = reductionAnchor; createGPUTileThreadReductionTransform(pm, tileThreadRedOptions); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); { OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName()); anchoredPM.addPass(createLinalgFoldUnitExtentDimsPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(createCSEPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createAnchoredPipelinePass(reductionAnchor, anchoredPM)); } pm.addPass(createDetensorizeTransformInsertionPass(reductionAnchor)); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); pm.addPass(createCanonicalizeExtPass()); pm.addPass(createRewriteInDPSTransformInsertionPass(reductionAnchor)); pm.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreter(true)); pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass()); { OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName()); anchoredPM.addPass(createTensorPadSpecializationPass()); anchoredPM.addPass(bufferization::createEmptyTensorEliminationPass()); pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>( createAnchoredPipelinePass(reductionAnchor, anchoredPM)); } } }
==TODO== deep into this pipeline as this pipeline enhance upstream linalg with fusion, tiling and so on.
byre-tensor-opt
func: createByreTensorOptPipeline
- replace func call to byteir runtime(byre) op(
byre::ComputeOp) - replace
mhlo::CustomCallOptobyre::CustomOp - convert some hlo ops to byre, do not use compiler but runtime implementation.
void mlir::populateHloToByreTensorPattern(
RewritePatternSet &patterns,
const llvm::StringMap<llvm::StringRef> &supportMap, bool appendArgTypes) {
patterns.add<ConvertToByrePattern<mhlo::AddOp>,
ConvertToByrePattern<mhlo::ConvertOp>,
ConvertToByrePattern<mhlo::TransposeOp, /*keepAttrs*/ true>>(
patterns.getContext(), supportMap, appendArgTypes);
patterns.add<ConvertCustomCallOpToByrePattern<mhlo::CustomCallOp>,
ConvertCustomCallOpToByrePattern<ace::CustomCallOp>,
ConvertGatherOpToByrePattern, ConvertScatterOpToByrePattern,
ConvertDotOpToByrePattern, ConvertDotGeneralOpToByrePattern,
ConvertConvOpToByrePattern, ConvertReduceOpToByrePattern,
ConvertReduceWindowOpToByrePattern,
ConvertSelectAndScatterOpToByrePattern>(patterns.getContext(),
appendArgTypes);
patterns.add<
ConvertConstLikeOp<mhlo::ConstantOp>, ConvertConstLikeOp<ace::ConstOp>,
ConvertReshapeOp<mhlo::ReshapeOp>, ConvertReshapeOp<ace::ReshapeOp>,
ConvertSliceOp, ConvertConcatenateOp>(patterns.getContext());
}
void createByreTensorOptPipelineImpl(OpPassManager &pm, std::string entryFunc,
bool appendArgTypes) {
pm.addPass(createFuncTagPass(
/*anchorTag=*/"",
getAttrPlaceholderName(ByreDialect::getEntryPointFunctionAttrName()),
entryFunc));
pm.addPass(createConvertFuncToByreTensorPass(appendArgTypes));
pm.addPass(createSymbolDCEPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(
createConvertHloToByreCustomPass(getCudaByreCustomConfig()));
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(
createConvertHloToByreTensorPass(appendArgTypes));
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
}
byteir-bufferize-opt
func: createByteIRBufferizeOptPipeline
- replace tensor::empty with bufferization::AllocTensorOp
- bufferize tensor to buffer
- 使用
memref::createFoldMemRefAliasOpsPass折叠 对 alias 的 load/store - 消除
memref::CopyOp,即尝试用src代替target,或target替换src,减少copy。 - 折叠 subview 的 subview
byteir 用了 oneshot bufferize 去将tensor转换成memref。
linalg-memref-opt
func: createLinalgMemrefOptPipeline
- replace memref::CopyOp with linalg::generic or func call.
void addGenericLinalgMemrefOptPasses(OpPassManager &pm) {
// TODO: change getByteIRElementwiseFusionAttrName to GPU specific codegen
// anchor tag
pm.addPass(createMemrefCopyToLinalgPass(
getAttrPlaceholderName(
byre::ByreDialect::getEntryPointFunctionAttrName()),
getByteIRElementwiseFusionAttrName().str(), true));
pm.addPass(createMemrefCopyToLinalgPass(
getByteIRReductionFusionAttrName().str(), "", false));
}
scf-opt
func: createSCFOptPipeline
- lower linalg to scf
- fold subview
- 合并循环轴
- 优化
arith::CmpIOp,常量推导
gpu-opt
func: createGPUOptPipeline
- element-wise 类型优化
- reduction 类型优化,将forall映射到gpu的block和thread
- 收集gpu kerenl,将其放入SymbolTable
remove-func-body
func: createRemoveFuncBodyPass
inline
func: mlir::createInlinerPass
decl: llvm-project/mlir/include/mlir/Transforms/Passes.td
gpu-launch-func-to-byre
func: createConvertGPULaunchFuncToByrePass
- 将gpu.launch_func 替换为 byre::computeOp
set-op-space
func: createSetOpSpacePass
set-arg-space
func: createSetArgSpacePass
byre-opt
func: createByreOptPipeline
- func call to byre
- memory planing
- some memref ops to byre
void createByreOptPipelineImpl(OpPassManager &pm, const std::string &entryFunc,
bool appendArgTypes,
bool disableMemoryPlanning) {
pm.addPass(createFuncTagPass(
/*anchorTag=*/"",
getAttrPlaceholderName(ByreDialect::getEntryPointFunctionAttrName()),
entryFunc));
pm.addPass(createConvertFuncAndCallToByrePass(appendArgTypes));
// only applied on entry point function
OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName());
if (!disableMemoryPlanning) {
// underlying memory of constant op cannot be reused
anchoredPM.addPass(createMemoryPlanningPass(/* alignment */ 128,
/* alloca */ false,
/* memory space */ 0,
/* callback */ nullptr));
anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
}
anchoredPM.addPass(createConvertMemrefToByrePass());
anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createAnchoredPipelinePass(
ByreDialect::getEntryPointFunctionAttrName(), anchoredPM));
pm.addPass(createCSEPass());
}
nvvm-codegen
func: createNVVMCodegenPipeline
- shm 计算及分配(根据 memref::AllocOp 统计需要多少shm并在最前面分配好内存)
- 简化地址计算
void createNVVMCodegenPipelineImpl(OpPassManager &pm,
const bool &useBarePtrCallConv) {
// TODO add target for supporting different SMs
// TODO use target to decide passes
pm.addPass(createCollectGPUKernelPass());
pm.addNestedPass<gpu::GPUModuleOp>(createShmAllocaToWorkgroupArg());
pm.addPass(createCSEPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(createConvertSCFToCFPass());
pm.addPass(createExtractAddressComputationPass());
pm.addPass(memref::createExpandStridedMetadataPass());
pm.addPass(createLowerAffinePass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(createSimplifyLinearizedIndexPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(createCSEPass());
pm.addNestedPass<gpu::GPUModuleOp>(
createGPUToNVVMExtPass(useBarePtrCallConv));
pm.addPass(createCSEPass());
pm.addPass(createReconcileUnrealizedCastsPass());
addMultiCSEPipeline(pm, 3);
}
translate_to_ptx
func: translateToPTX
- 将 ModuleOp 编译成 ptx
byre-host
func: createByreHostPipeline
IRProcessor.preprocess_pass
createCatPreprocessPipeline
这些是在mhlo做图优化
void createCatPreprocessPipelineImpl(OpPassManager &pm,
const std::string &convLayout) {
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createFuseBMMDimensionPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createMatmulLayoutTransformPass(true, "rcr"));
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createUnfuseBatchNormPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createHloFolderPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createLayoutTransformationPass(convLayout));
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createHloMoveDownPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizeExtPass());
}
IRProcessor.cat_opt_pass
createCatOptPipeline
- mhlo to cat
void createCatOptPipelineImpl(OpPassManager &pm, bool anchor_only,
bool aggressive_mode) {
if (anchor_only) {
OpPassManager anchoredPM(func::FuncOp::getOperationName());
anchoredPM.addPass(createFuseMhloToCatPass());
anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizeExtPass());
anchoredPM.addPass(createMhloToCatPass());
anchoredPM.addPass(createCanonicalizeExtPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(
createAnchoredPipelinePass(getByteIRCatFusionAttrName(), anchoredPM));
} else {
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createFuseMhloToCatPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizeExtPass());
if (aggressive_mode) {
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createMhloToCatPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizeExtPass());
}
}
}
IRProcessor.hlo_opt_pass
createHloOptPipeline
IRProcessor.ait_opt_pass
指定一部分op走ait,这个函数实现对应的逻辑。
Runtime
runtime python interface
brt py interface
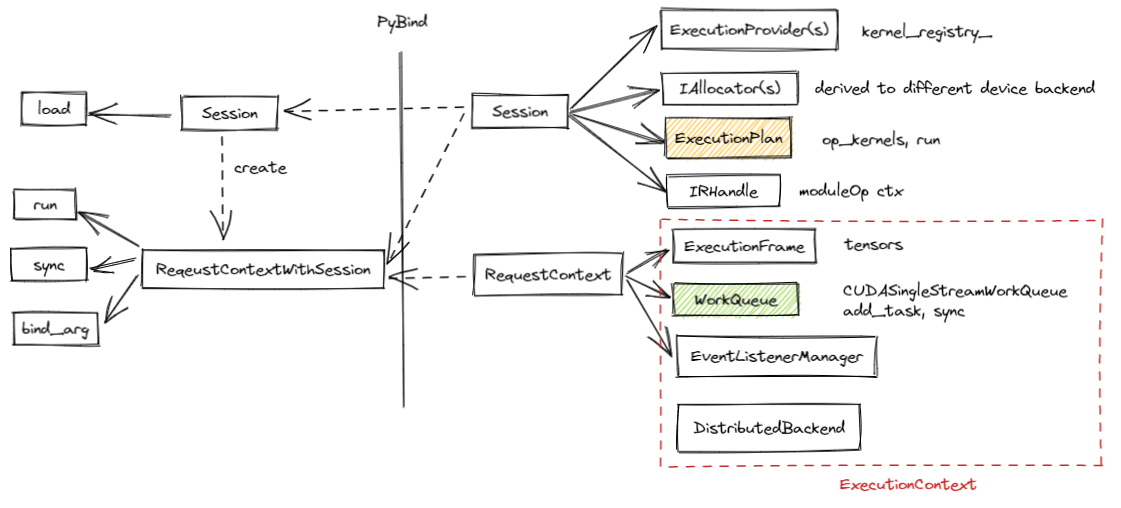
byre dialect 是 runtime 与 compiler 的交互对象。byteir 的 Session 对象用于管理 byre 对象的加载、执行、释放,RequestContext 对象则用于bind byre执行所需要的 input/output 等ctx。brt对外提供 python interface 时封装了 Session和ReqeustContextWithSession两个pyclass,其中:
Session几乎是封装了Sessioncpp class 的一些 interface,如loadmethod 用于加载模型文件(byre);另外增加了new_request_context方法,用于创建并获取ReqeustContextWithSession对象。ReqeustContextWithSession包含了Session以及RequestContext两个对象。比较困惑的是只暴露ReqeustContextWithSession不就可以了吗,为什么还需要把Seesion也暴露出去,因为后者作为成员对象被包含在前者内部了。
几个常用的 method:
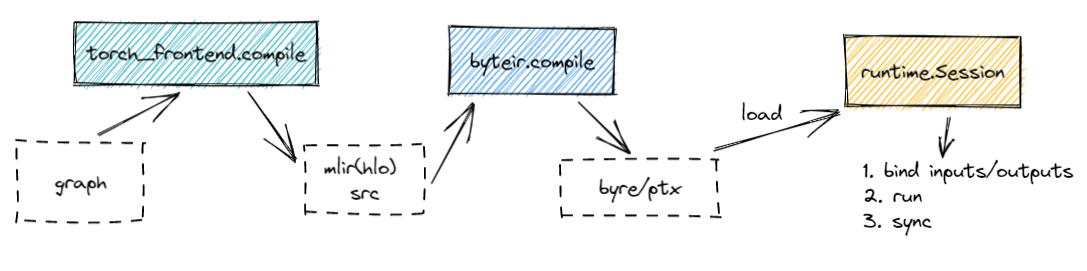
-
Session.load从文件中加载模型,创建并初始化 execution_plan。其中落盘的模型文件(byre)可以通过byre设计的格式进行序列化,如果序列化成MLIR的 bytecode 格式,load 方法会根据文件格式去对byre对象进行反序列化。最终加载到RAM中的是mlir的 ModuleOP 对象。 -
ReqeustContextWithSession.bind_arg实际调用的是RequestContext::BindArg方法。将buffer 指针 bind 到 ctx 中。实现如下:void BRTInferenceExecutionFrame::BindArg(size_t idx, const void *ptr) { int i = idx - info_.weights.size(); // if allocated, free it if (ctx_.is_io_allocated[i]) { ctx_.is_io_allocated[i] = false; auto allocator = info_.weight_and_ios_allocators[idx]; allocator->Free(ctx_.weights_and_ios[idx]); } ctx_.weights_and_ios[idx] = const_cast<void *>(ptr); }bind_arg参数中的 offset 是指当前bind第几个 arg,而不是指 ptr 的偏移。 -
ReqeustContextWithSession.finish_io_bindingctx中管理所有tensor(buffer),bind_arg方法 bindinput/output,finish_io_binding则为 weights 分配buffer。第一眼看到这个函数名以为是前面的bind是async的,需要在这里sync一下。void BRTInferenceExecutionFrame::FinishIOBinding() { size_t bound = info_.weights.size() + info_.graph_info.io_count; // alloc inputs/outputs for non-binding inputs/outputs size_t arg_idx = 0; for (size_t i = info_.weights.size(); i < bound; ++i, ++arg_idx) { if (ctx_.weights_and_ios[i] == nullptr) { ctx_.is_io_allocated[arg_idx] = true; auto allocator = info_.weight_and_ios_allocators[i]; ctx_.weights_and_ios[i] = allocator->Alloc(GetBytes(i)); } } } -
ReqeustContextWithSession.sync -
ReqeustContextWithSession.runRun a model for a given RequestContext.
实际调用的是不同 backend 的特定 execution_plan 对象:
common::Status Session::Run(RequestContext &request) { // Create ExecutionContext ExecutionContext ctx(request.frame_.get(), request.wq_.get(), execution_plan_->GetFrameStateInfo(), request.events_.get()); using State = ExecutionFrame::InternalState; Status status = request.frame_->GetIStateTransition() .Edge(State::BeforePrologue, State::MainLoop, [&] { return execution_plan_->ProloguePerFrame(ctx); }) .Invariant(State::MainLoop) .Apply(); if (!status.IsOK()) { return status; } return request.frame_->GetIStateTransition() .Edge(State::MainLoop, State::MainLoop, [&] { return execution_plan_->Run(ctx); }) .Apply(); }ProloguePerFrame在每个 frame 执行前 执行一次,StaticBRTExecutionPlan::ProloguePerFrame实现如下:common::Status StaticBRTExecutionPlan::ProloguePerFrame(const ExecutionContext &context) { // processes for (auto op : op_prologue_per_frame_) { common::Status status = op->ProloguePerFrame(context); if (!status.IsOK()) { return status; } } return common::Status::OK(); }为每个 op 执行前处理。如
ait的AITOpKernel需要在执行前准备 ait 的 runner。ExecutionPlan::Run先执行 shape kernel,然后分配中间内存,最后按拓扑序执行每个计算类型的op的run成员方法(OpKernel派生类的Run method。不同 backend 的 providers 实现并注册了各自的 op及其 RunImpl 方法,ExecutionPlan::Run实际调用到的则是这类RunImpl)。cudabackend 的Addop 的实现如下:template <typename T> common::Status Add<T>::RunImpl(const ExecutionContext &ctx) { auto tensor = GetMLIRValueFromOpArgIndex(info_, 0); auto shape = brt::ir::GetStaticShape(tensor); auto maybeN = LinearizedStaticShape(shape.value()); if (!maybeN.has_value()) { return Status(BRT, FAIL, "not supported shape"); } int64_t &n = maybeN.value(); auto p = MakeCUDAGridAndBlock(n); size_t dyn_shared_size = 0; // TODO move the following to util std::vector<void *> args; args.push_back(&p.first); // grid args.push_back(&p.second); // block args.push_back(&dyn_shared_size); // dyn_shared_size auto num_arg = GetOpArgNum(info_); // ptrs is used to make sure args still alive before AddTask is called std::vector<AsyncValueRef> ptrs(num_arg); for (unsigned int i = 0; i < num_arg; ++i) { auto tensor_id = GetTensorIndexFromOpArgIndex(info_, i); ptrs[i] = ctx.exec_frame->GetAsyncValueRef(tensor_id); args.push_back(&ptrs[i]); } args.push_back(&n); // n ctx.work_queue->AddEventWait(info_.GetOperation(), info_.GetDependency()); return ctx.work_queue->AddTask(0, (void *)add_kernel<T>, args.data()); }并没有实际立即执行这个 kernel,而是将其封装成 callable 对象添加到 work queue 中了。这为异步执行提供了潜力。而为 async run 插入同步指令的基础设施如下述。byteir 为 cuda backend 定义了如下的 task type:
enum CUDATaskType : int { kCompute = 0, kH2D = 1, kD2H = 2, kRecordEvent = 3, kWaitEvent = 4, kComputeDrv = 5, kD2D = 6, };其中
kRecordEvent和kWaitEvent则是用于插入同步指令。不同的 work queue 可以根据需要使用这些指令。byteir 的 cuda backend 目前只实现了CUDASingleStreamWorkQueueCUDAOneComputeTwoTransferWorkQueueCUDAExternalStreamWorkQueue这三类 work queue。第一个和第三个是 single stream的,所以 computed kernel 不需要插入复杂的 sync 指令,memcpy 前后根据 data-dependency 插入即可。第二个 work queue 是设计成三个 stream 共同 work,一个用于 compute,两个负责前后的内存搬移。所以 byteir 目前的 work queue 没有为 multistream 实现非常复杂的方案。single stream 的 work queue 即是最 naive 的按照拓扑序执行各个 task。
Byteir Runtime workflow:
Byteir Runtime component:
|---------|
| Session |
|---------|
/ | \
/ | \
/ | \
/ | \
|----------| |---------------| |--------|
| IRHandle | / | ExecutionPlan | | Device |
|----------| / |---------------| |--------|
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | |-----------| | |----------|
|---------------| | | Invokes | | |DeviceType|
| MLIRCTX | | | OpKernels | | | DeviceId |
|DialectRegistry| | |-----------| | |----------|
| ModuleOp | | v
|---------------| | |-------------|
| | Memory Plan |
\ |-------------|
\
\
\
\
v
|----------------|
| RequestContext |
|----------------|
/ | \
/ | \
|------------| |----------------| |-----------|
| ThreadPool | | ExecutionFrame | | WorkQueue |
|------------| |----------------| |-----------|
| |
v v
|------------------| |-------------------------|
|Holds all tensors:| | CUDAStreamWorkQueue |
|inputs | |CUDAMultiStreamWorkQueue |
|outputs | |CPUSingleThreadWorkQueue |
|constant | | CPUMultiThreadWorkQueue |
| ... | |-------------------------|