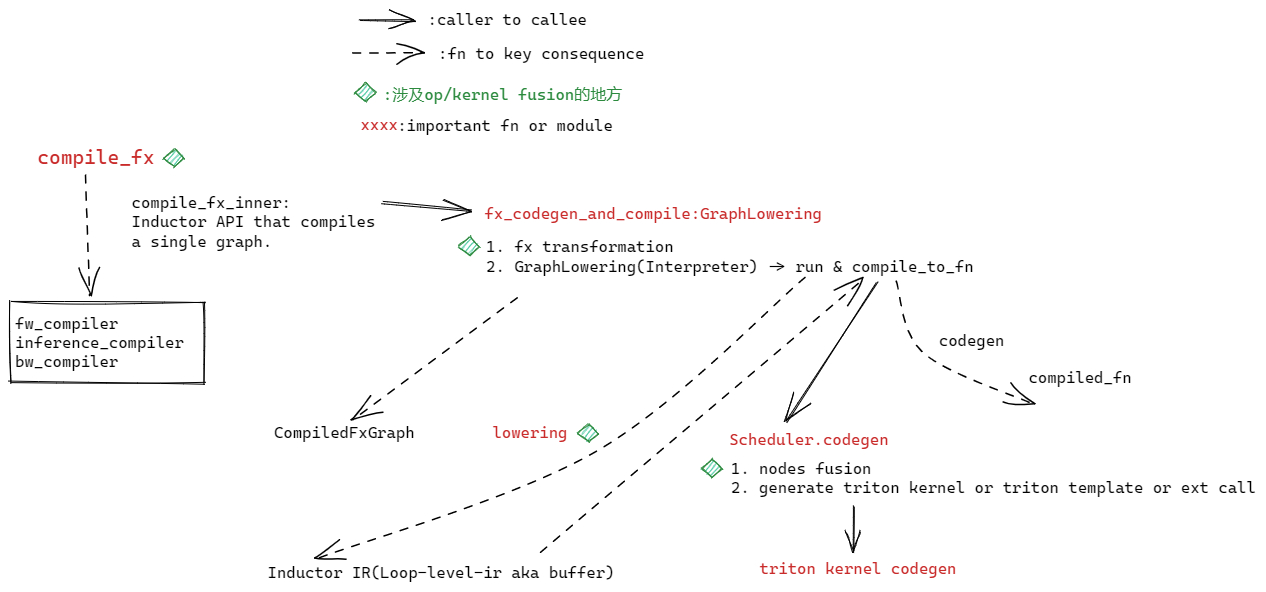
compile_fx
-
dynamo 注册 inductor
主入口是 compile_fx 函数,在dynamo中
@register_backend
def inductor(*args, **kwargs):
# do import here to avoid loading inductor into memory when it is not used
from torch._inductor.compile_fx import compile_fx
return compile_fx(*args, **kwargs)
-
compile_fx 核心逻辑
-
函数声明
def compile_fx(
model_: torch.fx.GraphModule,
example_inputs_: List[torch.Tensor],
inner_compile: Callable[..., Any] = compile_fx_inner,
config_patches: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
decompositions: Optional[Dict[OpOverload, Callable[..., Any]]] = None,
):
"""Main entrypoint to a compile given FX graph"""
-
dynamo之外的情形的处理
# NOTE. 根据传入的patches 去wrap inner_compile.
if config_patches:
with config.patch(config_patches): # type: ignore[attr-defined]
return compile_fx(
model_,
example_inputs_,
# need extra layer of patching as backwards is compiled out of scope
inner_compile=config.patch(config_patches)(inner_compile), # type: ignore[attr-defined]
decompositions=decompositions,
)
# NOTE. 生成 dynamic library,仅对cuda生效。`inner_compile_with_cpp_wrapper` 对 non-cuda 后端的branch,直接调用 inner_compile 完成编译;对 cuda 后端则先调用 inner_compile 编译并实际执行,然后将 cpp_wrapper 改成 True, 去生成 cpp wrapper code 以及生成动态库。
if config.cpp_wrapper:
with config.patch( # type: ignore[attr-defined]
{
"cpp_wrapper": False,
"triton.autotune_cublasLt": False,
"triton.cudagraphs": False,
# CudaWrapperCodeGen relies on kernel name to find the autotuned cubin file
"triton.unique_kernel_names": True,
}
), V.set_real_inputs(
example_inputs_
): # type: ignore[call-arg]
return compile_fx(
model_,
example_inputs_,
inner_compile=inner_compile_with_cpp_wrapper(inner_compile),
decompositions=decompositions,
)
recursive_compile_fx = functools.partial(
compile_fx,
inner_compile=inner_compile,
decompositions=decompositions,
)
# NOTE. 如果 gm 的返回值不是 tuple,则修改 gm 将其返回值改为tuple类型,然后返回 recursive_compile_fx 的编译结果。这是用于 non-dynamo 生成的计算图。
if not graph_returns_tuple(model_):
return make_graph_return_tuple(
model_,
example_inputs_,
recursive_compile_fx,
)
# NOTE. 处理 dynamo.export 生成的fx graph 中嵌入的 pytrees,调用 codegen.process_inputs 使得 inductor可以正常编译这个 graph.
if isinstance(model_, torch.fx.GraphModule):
if isinstance(model_.graph._codegen, _PyTreeCodeGen):
# this graph is the result of dynamo.export()
return handle_dynamo_export_graph(
model_,
example_inputs_,
recursive_compile_fx,
)
# Since handle_dynamo_export_graph will trigger compile_fx again,
# Move these passes after handle_dynamo_export_graph to avoid repeated calls.
model_ = pre_grad_passes(model_, example_inputs_)
# NOTE. 处理 non-dynamo 生成的 graph,inputs 没有被flat.
if any(isinstance(x, (list, tuple, dict)) for x in example_inputs_):
return flatten_graph_inputs(
model_,
example_inputs_,
recursive_compile_fx,
)
-
推理/训练通用的 forward graph 的compiler
# NOTE. 区别处理推理场景与训练场景的逻辑.
@dynamo_utils.dynamo_timed
def fw_compiler_base(
model: torch.fx.GraphModule,
example_inputs: List[torch.Tensor],
is_inference: bool,
):
# NOTE. 对推理场景做优化。尝试(1)常量折叠(2)替换随机函数(3)计算图拓扑序重排,graph重新生成,去除autograd生成的死节点。
if is_inference:
# partition_fn won't be called
joint_graph_passes(model)
num_rng_seed_offset_inputs = 2 if functorch_config.functionalize_rng_ops else 0
fixed = len(example_inputs) - num_example_inputs - num_rng_seed_offset_inputs
user_visible_outputs = set()
# NOTE. 是否保持outputs的stride,如果是单纯的推理场景,一般不太需要保持。
if config.keep_output_stride:
*_, model_outputs_node = model.graph.nodes
assert model_outputs_node.op == "output"
model_outputs, _ = pytree.tree_flatten(model_outputs_node.args)
num_model_outputs = len(model_outputs)
context = torch._guards.TracingContext.get()
# NOTE. joint-graph的outputs由原始计算图的outputs和保存给反向图的inputs组成,一般原始outputs都是在outputs的最前面,但是 aot-autograd 会把inplace updated tensors 放在最前面,这导致原始outputs的位置难以明确,所以需要用`original_output_start_index`去指明这个位置(根据mutated inputs数量即可获得)。
if context is not None and context.fw_metadata:
original_output_start_index = context.fw_metadata.num_mutated_inputs
else:
original_output_start_index = 0
# NOTE. 获取原始outputs的数量.
if isinstance(model_, torch.fx.GraphModule):
*_, orig_model_outputs_node = model_.graph.nodes
assert orig_model_outputs_node.op == "output"
orig_model_outputs, _ = pytree.tree_flatten(
orig_model_outputs_node.args
)
num_orig_model_outputs = len(orig_model_outputs)
else:
num_orig_model_outputs = num_model_outputs
assert num_orig_model_outputs <= num_model_outputs
# We makes the following assumption
# For inference
# len(orig_model_outputs) == len(model_outputs)
# For training
# len(orig_model_outputs) <= len(model_outputs)
# During training, most of the time the model_outputs starts with
# orignal module's outputs followed by saved activations.
# But this can be not true if the model have inplace updated tensors.
# AOTAutograd will make those tensors being returned before the orignal
# module's output.
# To make things safe, we'll use original_output_start_index field
# set by AOTAutograd to decide where the original module outputs start.
# NOTE. 遍历原始的outputs,填入`user_visible_outputs`,`GraphLowering`会根据这个set去判断是否考虑 keep outputs stride.
user_visible_outputs = {
n.name
for n in model_outputs[
original_output_start_index : original_output_start_index
+ num_orig_model_outputs
]
if isinstance(n, torch.fx.Node)
}
return inner_compile(
model,
example_inputs,
num_fixed=fixed,
cudagraphs=cudagraphs,
graph_id=graph_id,
is_inference=is_inference,
boxed_forward_device_index=forward_device,
user_visible_outputs=user_visible_outputs,
)
-
定义 fw_compiler, inference_compiler, bw_compiler
# NOTE. fw_compiler 是用于训练的。
fw_compiler = functools.partial(fw_compiler_base, is_inference=False)
# NOTE. `inference_compiler` 用于推理.
# NOTE. 如果开启了freezing功能且当前上下文关闭了grad,则生成infer用的compiler,其会调用 freeze 做常量折叠优化,算子layout优化等. 否则直接偏特化 fw_compiler_base
if config.freezing and not torch.is_grad_enabled():
inference_compiler = functools.partial(
fw_compiler_freezing,
dynamo_model=model_,
num_example_inputs=num_example_inputs,
inner_compile=inner_compile,
cudagraphs=cudagraphs,
graph_id=graph_id,
forward_device=forward_device,
)
else:
inference_compiler = functools.partial(fw_compiler_base, is_inference=True)
@dynamo_utils.dynamo_timed
def bw_compiler(model: torch.fx.GraphModule, example_inputs: List[torch.Tensor]):
fixed = count_tangents(model)
return inner_compile(
model,
example_inputs,
num_fixed=fixed,
cudagraphs=cudagraphs,
is_backward=True,
graph_id=graph_id,
boxed_forward_device_index=forward_device,
)
-
定义切分aot-autograd生成的joint-graph的函数
# NOTE. 该函数用于在训练中,对 aot-autograd 产生的 joint graph 进行切分,使用 min-cut-max-flow 算法对graph切分,用 recomputing 的代价减少内存开销(反向图的很多输入是正向图的中间结果,一般情况下需要对中间节点进行保存,以给反向图计算用,采用重计算的方式减少中间节点)。
def partition_fn(graph, joint_inputs, **kwargs):
joint_graph_passes(graph)
return min_cut_rematerialization_partition(
graph, joint_inputs, **kwargs, compiler="inductor"
)
-
调用aot_autograd进行计算图编译
# NOTE. 编译阶段需要在 fake mode下执行,以正确的做符号执行。`detect_fake_mode`从inputs推导当前graph的fake mode,如果没有推出来那么构造允许实例inputs作为输入的fake mode。在fake mode下,torch在调度op实现时会调度到FakeTensorMode下的diapatch,从而进行符号执行。如果没有强制使用fake-mode,torch也会根据inputs/outputs类型去推导调度到哪个后端,简单的情形下也是可行的,但是无法正确处理没有inputs的op。
# TODO: can add logging before/after the call to create_aot_dispatcher_function
# in torch._functorch/aot_autograd.py::aot_module_simplified::aot_function_simplified::new_func
# once torchdynamo is merged into pytorch
fake_mode = detect_fake_mode(example_inputs_) or torch._subclasses.FakeTensorMode(
allow_non_fake_inputs=True
)
tracing_context = (
torch._guards.TracingContext.get() or torch._guards.TracingContext(fake_mode)
)
with V.set_fake_mode(fake_mode), torch._guards.tracing( # type: ignore[call-arg]
tracing_context
), compiled_autograd.disable():
# NOTE. `aot_autograd`对graph进行反向图构建,调用`partition`对joint-graph进行切分,调用fw_compiler/bw_compiler 对切分出的fw/bw graph 进行编译,另外也会使用`inference_compiler`对推理场景的fw graph进行编译.
return aot_autograd(
fw_compiler=fw_compiler,
bw_compiler=bw_compiler,
inference_compiler=inference_compiler,
decompositions=decompositions,
partition_fn=partition_fn,
keep_inference_input_mutations=True,
)(model_, example_inputs_)
-
compile_fx_inner
inductor对fw/bw/infer graph 的编译都是在compile_fx_inner这个函数实现的。
-
函数声明和一些非核心的处理逻辑
@DebugContext.wrap
@torch.utils._python_dispatch._disable_current_modes()
@time_and_log(attr="compilation time (in seconds)")
def compile_fx_inner(
gm: torch.fx.GraphModule,
example_inputs: List[torch.Tensor],
cudagraphs: Optional[BoxedBool] = None,
num_fixed: int = 0,
is_backward: bool = False,
graph_id: Optional[int] = None,
cpp_wrapper: bool = False,
aot_mode: bool = False,
is_inference: bool = False,
boxed_forward_device_index: Optional[BoxedDeviceIndex] = None,
user_visible_outputs: FrozenSet[str] = frozenset(),
layout_opt: Optional[bool] = None,
):
"""
Inductor API that compiles a single graph.
If you change the argument list for this funtion, make sure you
also update the call to save_args_for_compile_fx_inner below accordingly.
"""
# NOTE. 如果graph中call op的数量为0,则直接返回,不需要编译优化.
if dynamo_utils.count_calls(gm.graph) == 0:
return make_boxed_func(gm.forward)
# NOTE. `save_args_for_compile_fx_inner`:
"""
This function is used to save arguments for a compile_fx_inner function call
to the file system. Later on one can replay the compile_fx_inner call
with the saved arguments using load_args_and_run_compile_fx_inner.
"""
if config.save_args:
save_args_for_compile_fx_inner(
gm,
example_inputs,
cudagraphs=cudagraphs,
num_fixed=num_fixed,
is_backward=is_backward,
graph_id=graph_id,
cpp_wrapper=cpp_wrapper,
aot_mode=aot_mode,
is_inference=is_inference,
boxed_forward_device_index=boxed_forward_device_index,
user_visible_outputs=user_visible_outputs,
layout_opt=layout_opt,
)
-
调用fx_codegen_and_compile进行计算图编译
if cudagraphs is None:
cudagraphs = BoxedBool(config.triton.cudagraphs)
# Inputs to fx_codegen_and_compile
graph_args = [gm, example_inputs]
graph_kwargs = {
"cudagraphs": cudagraphs,
"num_fixed": num_fixed,
"is_backward": is_backward,
"graph_id": graph_id,
"cpp_wrapper": cpp_wrapper,
"aot_mode": aot_mode,
"is_inference": is_inference,
"user_visible_outputs": user_visible_outputs,
"layout_opt": layout_opt,
}
compiled_graph: CompiledFxGraph = fx_codegen_and_compile(
*graph_args, **graph_kwargs # type: ignore[arg-type]
)
后处理(忽略cudagraph相关的逻辑分支)
# NOTE. post-process. 调用`align_inputs`处理inputs的内存对齐,对non-fixed inputs进行内存对齐检查,没对齐的话则调用`copy_misaligned_inputs`进行内存对齐处理(实际是用as_strided方法实现)。
# cudagraphs does its own aligning of inputs
if not cudagraphs:
new_callable = align_inputs(
compiled_graph.get_current_callable(), example_inputs, range(num_fixed)
)
if new_callable is not compiled_graph.get_current_callable():
compiled_graph.current_callable = new_callable
# aot autograd needs to know to pass in inputs as a list
compiled_graph._boxed_call = True
return compiled_graph
-
fx_codegen_and_compile
做一些autograd的后处理,然后用GraphLowering进行fx graph的lowering(GraphLowering.run)和codegen(Graphlowerin.compile_to_fn),生成CompiledFxGraph
# NOTE. 遍历node,将aten.view替换成aten.reshape
view_to_reshape(gm)
fake_mode = fake_tensor_prop(gm, example_inputs)
# NOTE. 处理`functionalized`后的graph,无效代码消除等.
with V.set_fake_mode(fake_mode): # type: ignore[call-arg]
# has some issues with memory in training
post_grad_passes(gm, is_inference=is_inference)
V.debug.fx_graph_transformed(gm, example_inputs)
with V.set_fake_mode(fake_mode): # type: ignore[call-arg]
graph = GraphLowering(
gm,
shape_env=shape_env,
num_static_inputs=num_fixed,
graph_id=graph_id,
cpp_wrapper=cpp_wrapper,
aot_mode=aot_mode,
user_visible_outputs=user_visible_outputs,
)
with V.set_graph_handler(graph): # type: ignore[call-arg]
graph.run(*example_inputs)
compiled_fn = graph.compile_to_fn()
compiled_graph = CompiledFxGraph(
compiled_artifact=compiled_fn,
cache_key=graph.cache_key,
artifact_path=graph.cache_path,
cache_linemap=graph.cache_linemap,
device_types=graph.device_types,
device_idxs=graph.device_idxs,
mutated_inputs=graph.mutated_inputs,
mutated_input_idxs=set(graph.mutated_input_idxs),
)
return compiled_graph
GraphLowering
-
Interpreter
-
声明和注释
按拓扑序对node进行解释执行。call_function和call_method的区别是:(1) call_function一般是torch.aten.mul这类op (2) call_method一般是 Tensor.add 这类method。
@compatibility(is_backward_compatible=True)
class Interpreter:
"""
An Interpreter executes an FX graph Node-by-Node. This pattern
can be useful for many things, including writing code
transformations as well as analysis passes.
Methods in the Interpreter class can be overridden to customize
the behavior of execution. The map of overrideable methods
in terms of call hierarchy::
run()
+-- run_node
+-- placeholder()
+-- get_attr()
+-- call_function()
+-- call_method()
+-- call_module()
+-- output()
"""
-
run核心逻辑
@compatibility(is_backward_compatible=True)
def run(self, *args, initial_env : Optional[Dict[Node, Any]] = None, enable_io_processing : bool = True) -> Any:
"""
Run `module` via interpretation and return the result.
"""
self.env = initial_env if initial_env is not None else {}
for node in self.module.graph.nodes:
# NOTE. 先检查当前node是否被执行过,应该是考虑到图中有环
if node in self.env:
continue
# NOTE. 调用 run_node 执行这个node,并将结果保存在env中
# NOTE. 调用 run_node 的方式是 self.run_node,类似 c++ 中 this指针,所以派生类的 run 会动态的调用到派生类的 run_node 的实现上。
try:
self.env[node] = self.run_node(node)
except Exception as e:
raise
if self.garbage_collect_values:
for to_delete in self.user_to_last_uses.get(node, []):
del self.env[to_delete]
# NOTE. 如果是output 节点,说明图已经执行完了,返回整个图的执行结果
if node.op == 'output':
output_val = self.env[node]
return self.module.graph.process_outputs(output_val) if enable_io_processing else output_val
-
run_node
@compatibility(is_backward_compatible=True)
def run_node(self, n : Node) -> Any:
"""
Run a specific node ``n`` and return the result.
Calls into placeholder, get_attr, call_function,
call_method, call_module, or output depending
on ``node.op``
Args:
n (Node): The Node to execute
Returns:
Any: The result of executing ``n``
"""
# NOTE. 保存当前node的meta信息到global的上下文(一个map)
with self._set_current_node(n):
# NOTE. 从 `env` 中获取当前node的操作数,函数`run`会将每个节点的执行结果保存在env,所以当前节点依赖的操作数应该可以从 `env`中获取。
args, kwargs = self.fetch_args_kwargs_from_env(n)
assert isinstance(args, tuple)
assert isinstance(kwargs, dict)
# NOTE. 根据当前节点的op类型选择对应的执行函数,如 call_function, call_method...
return getattr(self, n.op)(n.target, args, kwargs)
-
call_function
默认的实现是直接调用这个对应的函数实例target
def call_function(self, target : 'Target', args : Tuple[Argument, ...], kwargs : Dict[str, Any]) -> Any:
"""
Execute a ``call_function`` node and return the result.
"""
assert not isinstance(target, str)
# Execute the function and return the result
return target(*args, **kwargs)
-
GraphLowering
-
run_node核心逻辑
call_finction仅仅是实现将 op lowering到 Inductor IR,后处理还需要在合适的node进行realize。
def run_node(self, n: torch.fx.Node):
origins = {n}
# NOTE. 经过dynamo和functionlization之后,graph中都是call_function节点
if n.op == "call_function":
args, kwargs = self.fetch_args_kwargs_from_env(n)
origins |= gather_origins(args, kwargs)
with ir.IRNode.current_origins(origins), self.set_current_node(n):
...
elif n.op == "call_function" and n.target in layout_constraints:
# NOTE. 调用 call_function 函数进行lowering and codegen
args, kwargs = layout_constraints[n.target](n, *args, **kwargs)
result = self.call_function(n.target, args, kwargs)
...
else:
result = super().run_node(n)
# NOTE. 后处理 outputs中的stride,offset,使result保持stride order:`result = ir.ExternKernel.require_stride_order(result, stride_order)`
# require the same stride order for dense outputs,
# 1. user-land view() will not throw because inductor
# output different strides than eager
# long term the solution is to make view() always succeed
# with infallible strides.
# 2: as_strided ops, we need make sure its input has same size/stride with
# eager model to align with eager behavior.
as_strided_ops = [
torch.ops.aten.as_strided.default,
torch.ops.aten.as_strided_.default,
torch.ops.aten.as_strided_scatter.default,
]
is_output = any(user.op == "output" for user in n.users)
is_input_for_as_strided = any(
user.target in as_strided_ops for user in n.users
)
if (is_output or is_input_for_as_strided) and isinstance(
n.meta["val"], torch.Tensor
):
strides = n.meta["val"].stride()
dense = torch._prims_common.is_non_overlapping_and_dense(n.meta["val"])
# requiring a stride order for a non-dense output wouldn't
# recreate the same strides, and would fail with view, defer for now.
if dense and len(strides):
stride_order = ir.get_stride_order(strides)
if (
len(result.get_size()) == 4
and n in self.nodes_prefer_channels_last
and n.name not in self.user_visible_outputs
and not is_input_for_as_strided
):
stride_order = ir.NHWC_STRIDE_ORDER
result = ir.ExternKernel.require_stride_order(result, stride_order)
# NOTE. 后处理,判断是否对节点进行实例化(call result.realize_hint)
# NOTE. 选出了一些需要realize operand的op(needs_realized_inputs),检查当前节点的users中是否需要realize operand,是的话则进行realize处理。
# Realize if (1) any user need inputs realized, or (2) there is
# already too many reads and rematerializing can be bad.
num_users = len(set(n.users))
if num_users > 1 and isinstance(result, TensorBox):
for user in n.users:
if user.target in needs_realized_inputs:
# NOTE. 如果满足条件,最终会调用 realize()
result.realize_hint()
...
if user.target in need_fixed_layout:
result = ir.ExternKernel.require_stride_order(
result, ir.get_stride_order(n.meta["val"].stride())
)
# NOTE. 如果当前node结果是output,那么需要实例化。
if user.op == "output":
if isinstance(result.data.data, (Pointwise, Reduction)):
result.realize()
result.mark_reuse(len(n.users))
# NOTE. 如果当前node节点read数量大于阈值(典型值=8)则尝试实例化node,防止大量的重复计算。
# Realize if the IRNode already has accumulated lots of reads
if isinstance(result, TensorBox) and result.has_exceeded_max_reads():
# Prevent excessive accumulation in a computed buffer, when
# there are multiple branches each with small number of memory
# reads, but they converge to a user.
result.realize_hint()
...
self.register_users_of(result)
return result
-
call_function
def call_function(self, target, args, kwargs):
# NOTE. 处理 getitem,直接走eager的逻辑
if target is operator.getitem and isinstance(args[0], (list, tuple)):
return super().call_function(target, args, kwargs)
if hasattr(target, "_inductor_lowering_function"):
# passthrough lowerings from .pattern_matcher
return target(*args, **kwargs)
# NOTE. lowerings中没有注册对应target的lowering实现,如果允许fallback则走eager,否则抛出异常
if target not in lowerings:
...
try:
out = lowerings[target](*args, **kwargs)
return out
except Exception as e:
...
-
compile_to_fn
compile_fx中会调用compile_to_fn对Inductor IR进行codegen。compile_to_fn调用codegen函数进行codegen。
def codegen(self):
from .scheduler import Scheduler
self.init_wrapper_code()
self.scheduler = Scheduler(self.buffers)
assert self.scheduler is not None # mypy can't figure this out
# NOTE. 生成kernel
self.scheduler.codegen()
assert self.wrapper_code is not None
# # NOTE. 生成wrapper
return self.wrapper_code.generate()
buffers则是lowering的结果(Inductor IR),如下函数forward
def forward(x, y):
x = torch.ops.aten.sin(x)
z0 = torch.ops.aten.mm(x, y)
z1 = torch.ops.aten.cos(z0)
z2 = z0 + z1
return z2
经过lowering得到的ComputedBuffer如下:
计算图被拆分成三个stage(此时还未经过fusion,所以不一定是三个kernel,但是这个case中间的stage是mm,基本是确定要调库的,所以最终生成三个kernel),第一个stage计算sin(x),其result会realize到buf0(ComputedBuffer)中;mm对应的是第二个stage ExternKernelOut,其inputs包含buf0和arg1_1,后者是一个InputBuffer,会realize出buf1;最后一个stage计算 cos和add,realize出buf2。
[ComputedBuffer(name='buf0', layout=FixedLayout('cuda', torch.float32, size=[3, 4], stride=[4, 1]), data=Pointwise(
'cuda',
torch.float32,
def inner_fn(index):
i0, i1 = index
tmp0 = ops.load(arg0_1, i1 + 4 * i0)
tmp1 = ops.sin(tmp0)
return tmp1
,
ranges=[3, 4],
origin_node=sin,
origins={sin}
)), ExternKernelOut(name='buf1', layout=FixedLayout('cuda', torch.float32, size=[3, 6], stride=[6, 1]), inputs=[ComputedBuffer(name='buf0', layout=FixedLayout('cuda', torch.float32, size=[3, 4], stride=[4, 1]), data=Pointwise(
'cuda',
torch.float32,
def inner_fn(index):
i0, i1 = index
tmp0 = ops.load(arg0_1, i1 + 4 * i0)
tmp1 = ops.sin(tmp0)
return tmp1
,
ranges=[3, 4],
origin_node=sin,
origins={sin}
)), InputBuffer(name='arg1_1', layout=FixedLayout('cuda', torch.float32, size=[4, 6], stride=[6, 1]))], constant_args=(), kwargs={}, output_view=None), ComputedBuffer(name='buf2', layout=FixedLayout('cuda', torch.float32, size=[3, 6], stride=[6, 1]), data=Pointwise(
'cuda',
torch.float32,
def inner_fn(index):
i0, i1 = index
tmp0 = ops.load(buf1, i1 + 6 * i0)
tmp1 = ops.load(buf1, i1 + 6 * i0)
tmp2 = ops.cos(tmp1)
tmp3 = tmp0 + tmp2
return tmp3
,
ranges=[3, 6],
origin_node=add,
origins={cos, add}
))]
如果需要从Inductor接入后端,需要从_inductor/codegen中注册,参考_inductor/codegen/common.py:
# The code generated by Inductor consists of two main parts: kernel code and wrapper code.
# For any new backend looking to integrate with Inductor, customization of these two main
# parts are necessary to generate its specific code.
#
# Kernel code generation is determined by different Scheduling. Consequently, a new
# backend needs to provide a custom Scheduling for its unique kernel code generation. Currently,
# CppScheduling and TritonScheduling serve the C++/OpenMP and Triton backends, respectively.
#
# For the Wrapper, Inductor provides a WrapperCodeGen class to generate the Python wrapper code
# that bridges kernels. This allows out-of-tree backends to inherit from WrapperCodeGen,
# and override specific member functions to create backend-specific Python wrapper code.
#
# Other classes, such as CppKernel and TritonKernel, used for code generation, typically form part
# of the logic for either Scheduling or WrapperCodeGen. So the Scheduling and WrapperCodeGen interfaces
# provide flexibility to the backend. A backend can choose to implement these classes from scratch,
# or reuse them by extending and overriding as necessary. And Inductor provides the registration API,
# register_backend_for_device, to equip a new backend at runtime.
#
# Intel has developed a new backend on top of Triton to support Intel GPUs, leveraging these interfaces.
# This backend can be used as a reference:
# https://github.com/intel/intel-extension-for-pytorch/blob/5dcc9d57e5422cf295e1a1ee97896d6b6a554a85/intel_extension_for_pytorch/_inductor/__init__.py#L9
Scheduler
-
init
一些重要的逻辑实现在初始化阶段。__init__(self, nodes) 中的nodes即buffers,即Inductor IR的Buffer数组。这个函数(1)将ir.Buffer转换成ScheduerNode(2)node间依赖分析(3)以node为粒度进行fusion
def __init__(self, nodes):
super().__init__()
self.backends = {}
self.fuse_cache = {}
self.nodes = []
self.available_buffer_names = {
*V.graph.graph_inputs.keys(),
*V.graph.constants.keys(),
}
# NOTE. 将 no-op转换为`NopKernelSchedulerNode`,`ExterKernel`转为`ExternKernelSchedulerNode`,`ComputedBuffer`或`TemplateBuffer`转为`SchedulerNode`
self.nodes = [self.create_scheduler_node(n) for n in nodes]
# some new constants could have been created above
self.available_buffer_names.update(V.graph.constants.keys())
for node in self.nodes:
node.prune_deps()
self.name_to_node = {n.get_name(): n for n in self.nodes}
self.name_to_fused_node = None # set in fuse_nods()
# we handle mutation by renaming modified versions of the same
# buffer in the dependency graph to prevent cycles.
# mutation_renames: tracks the current name for a given buffer
# (changed once per mutation)
self.mutation_real_name = {}
# mutation_real_name: maps back to the original name for codegen
self.mutation_renames = {}
# NOTE. 添加node间依赖边;先进行alias分析,消除alias;处理mutation
self.compute_dependencies()
# NOTE. 后序遍历nodes,得到拓扑序的排序。
self.topological_sort_schedule()
# NOTE. 消除没有user的节点
self.dead_node_elimination()
# NOTE. 前面已经进行了依赖分析和拓扑排序,递归的统计每个节点的前驱节点,用于后面的fusion等分析。
self.compute_predecessors()
metrics.ir_nodes_pre_fusion += len(self.nodes)
V.debug.ir_pre_fusion(self.nodes)
self.num_orig_nodes = len(self.nodes)
self.name_to_fused_node = {n.get_name(): n for n in self.nodes}
# NOTE. 生成ForeachNodeScheduler, 用于lowering 例如torch._foreach_add op,便于对这类算子的horizontal fusion.
# NOTE. https://docs.google.com/document/d/1JLr5yMAR8TuKW78ixKeqzfDHhcazwxKo_JXQnP_-wyY/edit?kh_source=GDOCS#heading=h.8x4z4mmet3im
self.create_foreach_nodes()
self.topological_sort_schedule()
# NOTE. 对 ir.Buffer(SchedulerNode) 进行fuse.
self.fuse_nodes()
# NOTE. 递归的更新 node的last_usage,
self.compute_last_usage()
V.debug.ir_post_fusion(self.nodes)
V.debug.graph_diagram(self.nodes)
self.debug_draw_graph()
# used during codegen:
self.current_device = None
self.buffer_names_to_free = set()
self.buffer_names_no_longer_needed = set()
# fx graph node to the position it appears in the graph
# for debug attribution
self.origin_to_index = {}
log.info("Number of scheduler nodes after fusion %d", len(self.nodes))
-
fuse_nodes
对用到相同buffer的node尝试进行fusion。 TODO more detail
-
codegen
将nodes compile到triton kernel(如果是cuda 后端)。ir.Buffer在__init__中被转换为不同类型的SchedulerNode, codegen函数则分别将这些nodes逐个编译成triton kernel。
@dynamo_timed
def codegen(self):
for node in self.nodes:
# NOTE. wrapper_code 相关,TODO
self.enter_context(node)
self.buffer_names_no_longer_needed.update(node.last_usage)
# NOTE. codegen前获取这个node对应的device
if not isinstance(node, NopKernelSchedulerNode):
device = node.get_device()
if (
device != self.current_device
or node.is_extern()
or node.is_template()
):
self.flush()
if device != self.current_device:
if device.type == "cuda":
if self.current_device and self.current_device.type == "cuda":
V.graph.wrapper_code.codegen_device_guard_exit()
assert device.index is not None, "device should have an index"
V.graph.wrapper_code.codegen_device_guard_enter(device.index)
elif self.current_device and self.current_device.type == "cuda":
V.graph.wrapper_code.codegen_device_guard_exit()
self.current_device = device
self.buffer_names_to_free.update(node.last_usage)
# NOTE. 根据 node 类型选择对应的codegen实现。
# NOTE. template -> codegen_template
# NOTE. extern -> codegen_extern_call
# NOTE. foreach -> codegen_foreach
# NOTE. FusedSchedulerNode, SchedulerNode -> codegen_nodes
if node.is_template():
node, *epilogue = node.get_nodes()
self.get_backend(device).codegen_template(node, epilogue)
elif node.is_extern():
self.codegen_extern_call(node)
elif node.is_foreach():
self.get_backend(device).codegen_foreach(node)
elif isinstance(node, (FusedSchedulerNode, SchedulerNode)):
self.get_backend(device).codegen_nodes(node.get_nodes())
else:
assert isinstance(node, NopKernelSchedulerNode)
node.allocate()
if config.triton.debug_sync_kernel:
self.get_backend(device).codegen_sync()
self.available_buffer_names.update(node.get_names())
self.flush()
-
TritonScheduling
当device='cuda'时,get_backend会返回TritonScheduling对象,用于将node编译为triton kernel。
-
codegen_template
def codegen_template(self, template_node, epilogue_nodes):
"""
Codegen a triton template
"""
_, (numel, rnumel) = template_node.group
assert rnumel == 1
kernel, render = template_node.node.make_kernel_render(template_node.node)
with kernel:
for node in [template_node, *epilogue_nodes]:
node.mark_run()
partial_code = render()
for node in epilogue_nodes:
node.codegen(kernel.split_and_set_ranges(node.get_ranges()))
# finalize must be called after adding epilogue above
src_code = partial_code.finalize()
node_schedule = [template_node, *epilogue_nodes]
kernel_name = self.define_kernel(src_code, node_schedule)
self.codegen_comment(node_schedule)
kernel.call_kernel(kernel_name)
self.scheduler.free_buffers()
-
codegen_extern_call
最终会调用ir中的codegen方法。
def codegen_extern_call(self, scheduler_node: ExternKernelSchedulerNode):
assert isinstance(scheduler_node, ExternKernelSchedulerNode)
scheduler_node.allocate()
node = scheduler_node.node
node.codegen(V.graph.wrapper_code)
self.free_buffers()
-
codegen_foreach
def codegen_foreach(self, foreach_node):
from .triton_foreach import ForeachKernel
for partitions_with_metadata in ForeachKernel.horizontal_partition(
foreach_node.get_subkernel_nodes(), self
):
kernel = ForeachKernel()
for nodes, tiled_groups, numel, rnumel in partitions_with_metadata:
node_schedule = self.generate_node_schedule(nodes, numel, rnumel)
(
reduction_hint_val,
mutations,
index_dtype,
) = self.get_kernel_args(node_schedule, numel, rnumel)
self.codegen_node_schedule_with_kernel(
node_schedule,
kernel.create_sub_kernel(
*tiled_groups,
reduction_hint=reduction_hint_val,
mutations=mutations,
index_dtype=index_dtype,
),
)
src_code = kernel.codegen_kernel()
kernel_name = self.define_kernel(src_code, [foreach_node])
self.codegen_comment([foreach_node])
kernel.call_kernel(V.graph.wrapper_code, kernel_name)
self.scheduler.free_buffers()
-
codegen_nodes
调用codegen_node_schedule生成triton kernel,
def codegen_nodes(self, nodes):
"""
Given a set of pre-fused nodes, generate a Triton kernel.
"""
_, (numel, rnumel) = max(nodes, key=lambda x: int(x.is_reduction())).group
node_schedule = self.generate_node_schedule(nodes, numel, rnumel)
if schedule_log.isEnabledFor(logging.DEBUG):
schedule_log.debug("Schedule:\n %s", node_schedule)
return self.codegen_node_schedule(node_schedule, numel, rnumel)
triton kernel具体的生成是在做字符串拼接:
def codegen_kernel(self, name=None):
from triton import next_power_of_2
code = IndentedBuffer()
size_hints = [
next_power_of_2(V.graph.sizevars.size_hint(numel)) for numel in self.numels
]
if self.persistent_reduction:
assert self.inside_reduction
heuristics = "persistent_reduction"
elif self.inside_reduction:
heuristics = "reduction"
else:
size_hints.pop()
heuristics = "pointwise"
if name is None:
code.splice(
f"""
import triton
import triton.language as tl
from torch._inductor.ir import ReductionHint
from torch._inductor.ir import TileHint
from torch._inductor.triton_heuristics import AutotuneHint, {heuristics}
from torch._inductor.utils import instance_descriptor
from torch._inductor import triton_helpers
"""
)
if config.benchmark_kernel:
code.splice(
"""
from torch._dynamo.testing import rand_strided
from torch._C import _cuda_getCurrentRawStream as get_cuda_stream
import torch
from torch._inductor.triton_heuristics import grid
"""
)
argdefs, _, signature = self.args.python_argdefs()
# maps actual expression to SizeArg if its in sizevars replacements
for i, arg in enumerate(signature):
if (
isinstance(arg, SizeArg)
and arg.expr in V.graph.sizevars.inv_precomputed_replacements
):
signature[i] = SizeArg(
arg.name, V.graph.sizevars.inv_precomputed_replacements[arg.expr]
)
mutated_args = set()
for mutation in self.mutations:
if mutation in self.args.input_buffers:
mutated_args.add(self.args.input_buffers[mutation])
if (
mutation in self.args.inplace_buffers
and mutation not in V.graph.removed_buffers
):
mutated_args.add(self.args.inplace_buffers[mutation].inner_name)
if mutation in self.args.output_buffers:
mutated_args.add(self.args.output_buffers[mutation])
mutated_args = sorted(mutated_args)
triton_meta = {
"signature": signature_to_meta(signature, size_dtype=self.index_dtype),
"device": V.graph.scheduler.current_device.index,
"device_type": V.graph.scheduler.current_device.type,
"constants": {},
"mutated_arg_names": mutated_args,
"autotune_hints": set(self.autotune_hints),
"kernel_name": "DESCRIPTIVE_KRNL_NAME",
}
for tree in self.range_trees:
if tree.prefix != "r" or self.inside_reduction:
sizearg = SizeArg(f"{tree.prefix}numel", tree.numel)
signature.append(sizearg)
triton_meta["signature"][len(argdefs)] = signature_of(
sizearg, size_dtype=self.index_dtype
)
argdefs.append(f"{tree.prefix}numel")
# constexpr version causes issues, see
# https://github.com/pytorch/torchdynamo/pull/1362
# triton_meta["constants"][len(argdefs)] = V.graph.sizevars.size_hint(
# tree.numel
# )
# argdefs.append(f"{tree.prefix}numel: tl.constexpr")
triton_meta["configs"] = [config_of(signature)]
for tree in self.range_trees:
if tree.prefix == "r" and (
not self.inside_reduction or self.persistent_reduction
):
continue
if tree.prefix == "x" and self.no_x_dim:
continue
argdefs.append(f"{tree.prefix.upper()}BLOCK : tl.constexpr")
if self.inside_reduction:
reduction_hint = self.reduction_hint
heuristics_line = f"""
@{heuristics}(
size_hints={size_hints!r},
reduction_hint={reduction_hint},
filename=__file__,
meta={triton_meta!r}
)
@triton.jit
"""
else:
tile_hint = ""
if len(size_hints) == 2:
if len(signature) == 4: # input, output and 2 args
tile_hint = "tile_hint=TileHint.SQUARE,"
else:
tile_hint = "tile_hint=TileHint.DEFAULT,"
heuristics_line = f"""
@{heuristics}(size_hints={size_hints!r}, {tile_hint}filename=__file__, meta={triton_meta!r})
@triton.jit
"""
code.splice(heuristics_line)
code.writeline(f"def {name or 'KERNEL_NAME'}({', '.join(argdefs)}):")
self.codegen_body()
with code.indent():
self.codegen_static_numels(code)
for old, new in self.args.aliases():
code.writeline(f"{old} = {new}")
code.splice(self.body)
if config.benchmark_kernel:
code.splice(self.codegen_kernel_benchmark())
if name is not None:
return code.getvalue()
return code.getvalue()
-
Node
-
BaseSchedulerNode
class BaseSchedulerNode:
def __init__(self, scheduler: "Scheduler", node: ir.Buffer):
self.scheduler: Scheduler = scheduler
self.node: ir.Buffer = node
self.users: Optional[List[NodeUser]] = None
self.inverse_users: List[BaseSchedulerNode] = []
self.set_read_writes(node.get_read_writes())
self.recursive_predecessors: Optional[Set[str]] = None
self.min_order: Optional[int] = None
self.max_order: Optional[int] = None
self.last_usage: Set[str] = None # buffers that won't be used after this kernel
self.written = False
-
ExternKernelSchedulerNode
class ExternKernelSchedulerNode(BaseSchedulerNode):
def debug_str_extra(self) -> str:
return f"{self.get_name()}.node.kernel = {getattr(self.node, 'kernel', None)}"
def is_extern(self):
return True
def has_side_effects(self):
return hasattr(self.node, "has_side_effects") and self.node.has_side_effects()
def can_inplace(self, read_dep: dependencies.MemoryDep):
if self.get_aliases() or self.is_template():
return False
if read_dep.name not in self.scheduler.name_to_node:
# don't allow reuse of an 'input' buffer, we don't own it
# (would this have been fixed if I tracked mutations properly above?)
return False
if not isinstance(
self.node, (torch._inductor.ir.AllReduce, torch._inductor.ir.InPlaceHint)
):
# TODO make this a property of the IR
return False
if len(self.read_writes.writes) == 1:
write_dep = next(iter(self.read_writes.writes))
return read_dep.numbytes_hint() == write_dep.numbytes_hint()
return False
-
SchedulerNode
只有ir.ComputedBuffer才转换到SchedulerNode
class SchedulerNode(BaseSchedulerNode):
def __init__(self, scheduler: "Scheduler", node: ir.ComputedBuffer, group_fn):
super().__init__(scheduler, node)
(
self._sizes,
self._body,
) = node.simplify_and_reorder()
self.group = (node.get_device(), group_fn(self._sizes))
if self.is_template():
self.set_read_writes(node.normalized_read_writes())
else:
self.set_read_writes(
dependencies.extract_read_writes(
self._body, *self._sizes, normalize=True
)
)
-
NopKernelSchedulerNode
class NopKernelSchedulerNode(BaseSchedulerNode):
pass
-
FusedSchedulerNode
class FusedSchedulerNode(BaseSchedulerNode):
"""
This is a "fake" scheduler node that represents a group of scheduler nodes
that are meant to be fused together. The way it does this is by maintaining
its unmet dependencies as the union of its constituent nodes.
"""
aot_autograd
TODO 反向图构建和图切分
lowering
-
lowerings
lowering.py 中实现了aten ops到Inductor IR(loop-level-ir)的映射,每个ops会被转换成 TensorBox或者View,前者代表这个op会产生新的tensor,而后者表示op的返回值是已有的tensor的view。op的计算逻辑保存在inner_fn中,op的类型有两个大类,分别是Pointwise和Reduction,两种在循环上行为不同的类型(很难fuse在一起)。
-
register_lowering
用于注册lowering的实现,将其存到全局 map lowerings中。
-
make_pointwise
创建pointwise类型op的表达,即实例化一个Pointwise对象。其核心是构造inner_fn,因为pointwise类型算子的行为几乎是一样的,所以这个函数就像模板函数一样为pointwise ops实例化Inductor IR。
-
make_reduction
同样的,make_reduction函数用于实例化Reduction对象,相比Pointwise多了reduce轴的信息。
-
xxxView
对于viewlike-ops,则实例化View对象,如:
@register_lowering(aten._unsafe_view, type_promotion_kind=None)
@register_lowering(aten.view, type_promotion_kind=None)
@register_lowering(aten.reshape, type_promotion_kind=None)
def view(x, sizes):
assert isinstance(x, TensorBox)
assert isinstance(sizes, (list, tuple))
return TensorBox(View.create(x.data, sizes))
-
realize
Inductor IR的设计中,TensorBox都是逻辑节点(简单的理解:是存在于寄存器中的变量,不会真的为其分配RAM用于实例化,想要拿到这个节点的result必须要按照inner_fn描述的计算逻辑算一遍),只有在realize后这个节点才会被分配内存(后续节点要访问这个节点的result,可以直接从内存中获取结果,而非recompute)。Inductor对于节点的realize从代码上看不是结构化的,而是散落在很多地方。
在lowering的实现中,有些ops会显示的要求realize,如:
@register_lowering(aten.bernoulli_, type_promotion_kind=None)
def bernoulli_(x, *args):
assert config.fallback_random or x.get_device() == torch.device(
"cpu"
), "this should be handled in decomps unless config.fallback_random or the device is CPU"
x.realize()
ir.InplaceBernoulliFallback(x, *args)
return x
ir
GraphLowering.run通过调用注册在lowerings中的实现,将aten ops转换为 Inductor IR.
-
Inductor IR的设计
""" [Note: Inductor IR]
Inductor's IR is produced by executing 'lowering' code (see lowering.py). Each
lowering is registered to a particular aten operator, and expects inputs that
correspond to the aten schema. However, in place of torch Tensor inputs, lowerings
expect Inductor TensorBox inputs.
TensorBox IR represents torch tensors. Tensors are sometimes single objects owning
storage, and sometimes views of another Tensor's storage. Mutating tensor operations
(such as add_()) affect the underlying storage and any associated views. Other operations
(such as .t_()) update metadata about the current view but don't modify the underlying storage.
To model this in Inductor, the IR distinguishes between TensorBox, View, StorageBox and Buffer.
TensorBox is the top level IR construct that any lowering should produce and maps to a torch.Tensor
output from an operation. But just as torch.Tensors take different forms, TensorBox IR can
reference View IR or directly reference StorageBox IRs.
Some Inductor lowerings produce new sets of 'Box'es, while others (such as .t() or other view ops)
may take an existing TensorBox and point it to a new underlying View IR.
Tensors that directly own storage are represented as a chain of:
TensorBox -> StorageBox -> Buffer
where Buffer is a simple (1D) allocation, and StorageBox introduces the concept of a Layout.
If you mutate the data of such a tensor, we swing the StorageBox pointer to point to a new buffer
(leaving the old buffer unmodified and functionalizing the operation).
Tensors backed by views add one more indirection to the IR.
TensorBox -> View -> StorageBox -> Buffer
In these cases, the underlying StorageBox/Buffer will be shared with the pre-view TensorBox.
"""
Inductor IR主要包含Buffer、Loops、TensorBox 对计算图进行建模。其中,
(1)TensorBox对位的是torch的tensor,是tensor的抽象表达,表示每个node产生的结果,StorageBox对位的是torch tensor的storage,表示真实的tensor对象,StorageBox对象会对应一个Buffer,所以 TensorBox -> StorageBox -> Buffer。torch中的viewlike-ops不会产生新的storage,而是一个view,Inductor IR 用 View去表达这种tensor,即与已有的tensor共享storage的类型,所以也有TensorBox -> View -> StorageBox -> Buffer
(2)Buffer对应的是实际物理内存,可以派生出InputBuffer,ComputedBuffer,InputsKernekl,TemplateBuffer,ExternKernel等。codegen的输入是Buffers,每个buffer节点对应一个kernel或外部函数调用。特别的,ComputedBuffer中的data成员对象是Loops类型,表示当前ComputedBuffer做了哪些计算逻辑。
(3)Loops是计算逻辑的抽象,其派生出Pointwise,Reduction等,对不同类型ops进行建模。Loops对象存在于ComputedBuffer中,表示这个buffer会进行的计算逻辑。
TODO 补一张基于IRNode派生的类的关系图。
-
realize
IRNode在realize之前是可以fuse的,realize之后结果会写到真实的内存,即当前节点的result可以直接从内存中获取,而不需要重计算出这个结果。所以可以推测IRNode的设计,以realize的IRNode作为codegen对象,这个IRNode的计算逻辑记录在Loops的inner_fn对象中。
def realize(self):
"""
If the IRNode refers to data which has not been materialized (e.g.,
it is a Pointwise/Reduction that could potentially have more
compute fused into it), realize the IRNode into physical memory,
ending the possibility of fusing into it, but allowing, e.g., multiple
users to access the data without having to recompute.
Check StorageBox.realize for a particularly notable implementation.
TODO(ezyang): I think, in principle, every IRNode should have an
implementation of this, and most of the time no-op is OK, but you
really do have to audit each IRNode for this, so for now, raise
an error if it's not implemented. Note that some code in graph.py
will catch this thrown error and suppress it with a warning.
"""
那么在合适的位置(tensor)进行realize则是inductor在lowering过程中的核心。整体上看,应该在什么地方realize并没有一个很统一的处理,而是分散在很多地方,但其原则是尽量用重计算减少访存开销。
-
reduce op 会进行realize
def make_reduction(reduction_type: str, override_return_dtype=None):
def inner(x, axis=None, keepdims=False, *, dtype=None):
kwargs = _make_reduction_inner(
x,
axis=axis,
keepdims=keepdims,
dtype=dtype,
override_return_dtype=override_return_dtype,
)
result = Reduction.create(reduction_type=reduction_type, **kwargs)
if isinstance(
result.data.data, Reduction
): # Only realize if reduction isn't unrolled
result.realize()
return result
return inner
-
GraphLowering
在run_nodes中,如果(1)users要求当前节点需要realize(2)当前节点的被读的次数超出阈值,recompute代价较大。当满足其中一个条件则会realize。
-
op lowering
在lowering aten ops到Inductor IR时,一些实现会调用realize或make_reuse进行realize
-
StorageBox.realize
realize实则是实例化了self.data对象(ComputedBuffer),注意到实例化ComputedBuffer时传入的self.data是StorageBox自身的data成员对象,也就说StorageBox.data在realize之前是Loops对象,之后是ComputedBuffer
def realize(self):
if isinstance(
self.data,
(
ComputedBuffer,
InputsKernel,
InputBuffer,
ReinterpretView,
TemplateBuffer,
),
):
return self.data.get_name()
assert isinstance(self.data, (Pointwise, Reduction)), type(self.data)
origin_node = self.data.get_origin_node()
traceback = self.data.get_traceback()
self.data = ComputedBuffer(
name=None,
layout=FlexibleLayout(
device=self.data.get_device(),
dtype=self.data.get_dtype(),
size=self.data.get_size(),
),
data=self.data,
)
self.data.name = V.graph.register_buffer(self.data)
self.data.origins = self.origins
self.data.origin_node = origin_node
self.data.traceback = traceback
return self.data.name
-
LoopBody
class LoopBody:
"""
Captures the body of a Loops subclass into an FX graph. Persists any
indexing simplifications and makes it easier to analyze loop bodies.
"""
是用于拼接Loops的辅助类,如在simplify_and_reorder函数中将当前节点(loop body)拼接进ComputedBuffer的loop body中。
def simplify_and_reorder(self):
"""
This is a main place where we do loop transformations in a
backend-agnostic way.
Here we:
1) Remove any 1 dimensions
2) Fuse contiguous dimensions together
3) Reorder dimensions based on stride orders
"""
Decompositions
-
core_aten_decompositions
定义pytorch/torch/_decomp/init.py中,是从aten op分解的实现中筛选出的由CoreAten Ops实现的集合。
-
get_decompositions
register_lowering会将aten ops的分解的实现注册到global_decomposition_table,get_decompositions则是根据输入的aten ops,返回对应的注册的实现。